How can I prevent diabetes naturally
This article focuses on the two most common types of diabetes – type 1 and type 2, as well as the role of hormones such as insulin and glucagon in the body. Diabetes occurs when there is insufficient insulin production or ineffective response by the body’s tissues, leading to disrupted sugar metabolism and elevated blood sugar levels. High blood sugar can cause damage to vital organs in the body over time. Type 2 diabetes results from the body’s inability to maintain regular blood sugar levels despite producing insulin. Obesity is a key factor in the development of insulin resistance and high blood sugar in these patients. Managing diabetes involves maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. In cases where lifestyle changes are not enough, medication such as oral hypoglycemic pills or insulin injections may be required to control blood sugar levels and prevent long-term complications.
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, is a disease caused by an immune reaction (Type 1A) and is a known heterogeneous disorder caused by mutations (autosomal recessive and X-dependent recessive), as well as multigene/monogenic inheritance. It accounts for 5 to 10 percent of all types of diabetes. In this type of diabetes, beta cell destruction occurs in the pancreas due to the “cellular immune response” that causes cell damage.
Despite these breakdowns, markers including insulin antibodies, GAD autoantibodies (GAD65), tyrosine phosphatase autoantibodies, IA-2, and IA-2β are released into the bloodstream, and these markers can be seen in 85 to 90% of patients. A link has also been found between specific acne and this type of diabetes. As the beta cells are destroyed by lymphocytes, insulin secretion decreases, and blood sugar cannot be regulated, leading to hyperglycemia.
Hyperglycemia typically occurs after the loss of 80 to 90% of beta cells, and the patient needs external insulin to prevent ketosis, control hyperglycemia, and manage fat and protein metabolism. In the past, type 1 diabetes was commonly referred to as adolescent diabetes because it was more prevalent in childhood. However, this condition can affect people of any age and is caused by the body’s autoimmune system, which attacks the pancreas using its antibodies, preventing it from producing insulin.

Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, can be caused by genetic factors as well as defective beta cells in the pancreas. This disease puts a person at significant risk for various health problems such as diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, heart disease, and stroke. The only way to regulate insulin levels is through injection of insulin under the skin, and there are various types of insulin available in the market.
Insulin pumps provide a method of insulin injection that closely mimics the normal secretion of insulin from the pancreas. The pump is a small device that consists of an insulin reservoir, an injection kit with a needle and a rubber tube, and a program that automatically injects the appropriate insulin concentration under the skin over 24 hours. The diabetic can also regulate the time and amount of insulin needed for meals, and newer pumps can calculate the insulin amount needed based on current blood sugar levels and carbohydrate intake.
One of the main obstacles to using insulin pumps is their high cost.
On the other hand, type 2 diabetes, also known as non-insulin dependent diabetes, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin, which is naturally produced in the pancreas and used to transfer sugar from the bloodstream to cells as energy. Over time, the pancreas may become damaged and may not be able to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels.
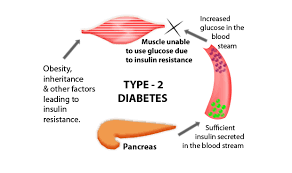
When there is insufficient insulin production or its ineffective use by the body, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, and the body lacks energy. The exact cause of this condition is still unknown, but it could be due to malfunctioning pancreatic cells or disrupted cellular communication. Additionally, some individuals might produce an excessive amount of glucose in their liver, and there could be a genetic predisposition to type 2 diabetes and obesity, increasing the risk of developing this disease. Ongoing research is aimed at uncovering the causes of type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is also known as adult-onset diabetes since 95% of the cases are related to this form of diabetes. In the past, it was more commonly seen in adults, but with the rising number of overweight children and adolescents, the disease has also affected people in this age group. Type 2 diabetes is less severe than type 1 diabetes, but neglecting it can have severe consequences. These consequences are primarily observed in the capillaries responsible for supplying blood to the kidneys, nerves, and eyes. Type 2 diabetes is also referred to as non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body cannot use insulin effectively or when it does not produce enough insulin. The pancreas still produces some insulin, but it is not enough for the body’s needs, or the cells have become resistant to it. Insulin resistance is usually found in fat, liver, and muscle cells. Being overweight, by as little as 20%, can increase the risk of developing this disease and its complications. This condition causes the pancreas to work harder to produce more insulin, but the insulin is still not sufficient to regulate blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease, and patients require diabetes medications to manage their condition. Recent studies have suggested that implanting polymer sponges into the body tissues of patients with type 2 diabetes could restart the relationship between fat and other body parts, preventing weight gain. Researchers at the University of South Carolina found that obese mice with type 2 diabetes, fed a high-fat diet, gained less weight and had lower blood sugar levels after three weeks of being implanted with polymer sponges compared to untreated mice. These findings may pave the way for new treatments for type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a growing concern for pregnant women due to changes in lifestyle and diet in recent years. It is a condition that causes elevated blood sugar levels during pregnancy and usually occurs between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Having gestational diabetes does not necessarily mean you had diabetes before or after childbirth, but it does increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. The exact cause of gestational diabetes is unknown, but hormonal changes during pregnancy, such as increased levels of human placental lactogen (HPL) and insulin resistance, may play a role.
During pregnancy, the body becomes less sensitive to insulin, which is responsible for transporting glucose into cells to provide energy. As a result, more glucose remains in the bloodstream, potentially leading to gestational diabetes. Doctors may perform a glucose challenge test to detect the disease during pregnancy, which involves drinking a glucose solution and having a blood test an hour later. The underlying cause of gestational diabetes remains a topic of ongoing research.

If your doctor suspects that your blood sugar is high, they may recommend an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT). Gestational diabetes is classified into two types: type 1 gestational diabetes can usually be controlled with a proper diet, while type 2 gestational diabetes requires insulin or oral medications to manage the condition. Treatment for gestational diabetes depends on your blood sugar levels throughout the day. In most cases, your doctor will recommend monitoring your blood sugar levels before and after meals, along with a healthy diet and regular exercise. In some cases, insulin injections may be prescribed.
Studies show that only 10 to 20 percent of women with gestational diabetes require insulin injections during pregnancy to control their blood sugar levels. Failure to manage gestational diabetes can result in high blood pressure during pregnancy, which may pose potential risks to your baby. These risks include high birth weight, breathing difficulties, low blood sugar, and shoulder dystocia.
Genetic Defects of Beta Cells:
Neonatal diabetes mellitus is a diverse group of diseases that affect infants up to 6 months old and occur in one out of every 200,000 live births. These babies are small during pregnancy and have decreased subcutaneous fat. Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous group of diabetics caused by genetic mutations, resulting in impaired insulin secretion. These mutations are estimated to cause 5% of all types of diabetes; however, accurate diagnosis is essential for treatment, prognosis, and risk to family members.
The most common type is maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), usually characterized by increased blood sugar at a young age (under 25 years). The inheritance of this type is “autosomal dominant,” and mutations in six gene loci have been identified, the most common being the “HNF-1α” mutation on chromosome 12 in the hepatic transcription factor. Mutations in the glucokinase gene, located on the 7p chromosome, result in the production of a defective molecule that converts glucose to glucose-6-phosphate and stimulates insulin secretion.
Higher levels of glucose are needed to lead to normal insulin secretion in these mutations. Other mutations in transcription factors, such as “HNF-4α,” “HNF-1β,” “IPF-1,” and “NeuroD1,” are rarer. Genetic testing for this type is recommended when the age of onset of diabetes is low, unusual symptoms are observed depending on type 1 and type 2 diabetes, or strong family history. Spot mutations on “exclusively mitochondrial DNA” inherited from the mother (NIDDM disorder) are associated with diabetes and deafness. The most common form of the 3243 position mutation in the tRNA is the leucine gene.
Genetic Insulin Dysfunction:
In this type of diabetes, women may exhibit masculine traits and have enlarged ovarian cysts. In the past, this syndrome was considered a type of insulin resistance. Leprachaunism and Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome are two syndromes in children where the patient has severe insulin resistance.
Extrinsic Pancreatic Diseases:
This disease is a complication of chronic “pancreatitis.” In this type of disease, the entire endocrine glands of the pancreas are destroyed, and these patients are more likely to develop hypoglycemia following treatment. Besides pancreatitis, diabetes can be a complication of any damage to the pancreas, including infections, pancreatic resection, and pancreatic cancer.
Endocrine Disorders:
Several hormones can counteract the function of insulin, and excessive secretion of any of them can lead to the disease. This disorder is more common in people who are already predisposed to diabetes due to deficient insulin secretion. Increased growth hormone and cortisol are common hormonal disorders leading to diabetes.

Diabetes Insipidus:
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a rare condition where the kidneys are unable to retain water. It is important to note that this condition does not cause high blood sugar levels, unlike diabetes mellitus. These two conditions are not related, and diabetes mellitus is more common. Diabetes insipidus can affect anyone, not just those with diabetes. Unlike diabetes mellitus, DI is caused by abnormal hormone production in the brain that prevents excessive urination and water loss. Without this hormone, the kidneys continuously produce urine.
Drug or chemical-induced diabetes:
In rare cases, the beta cells can be irreversibly destroyed due to the use of Vacor (an anti-mouse toxin) or intravenous pentamidine. Some medications can also interfere with insulin function, such as nicotinic acid and glucocorticoids. Certain drugs that are commonly used and considered safe are associated with an increased risk of diabetes, including thiazide antihypertensive drugs, statins, and beta-blockers. Although studies show a minimal increase in risk with statins, this does not justify discontinuing or reducing their use.
Pre-diabetes:
Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. It is often asymptomatic, unlike the acute symptoms of diabetes mellitus. However, some warning signs of pre-diabetes include dark skin, lack of sleep, decreased physical activity, blurred vision, increased thirst, and slow-healing ulcers. More than 86 million people in the United States over the age of 20 are pre-diabetic, which can lead to type 2 diabetes if left untreated. The American Diabetes Association estimates that over 9% of the US population had diabetes in 2012.
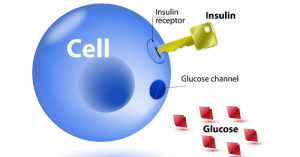
Glucose and Insulin:
The impairment of the body’s ability to use glucose is a characteristic of diabetes. Glucose is a simple sugar that provides energy to every cell in the body. It is obtained from the food we eat, and the cells break it down and store the energy. The body always tries to maintain the glucose level in the blood at an appropriate level, which is necessary for providing energy to the cells throughout the day.
When we eat food, the glucose is released into the digestive tract and then into the bloodstream. The body converts excess glucose into glycogen and stores it in the liver and muscles to provide energy during periods of hunger. Insulin and glucagon are two hormones released by the pancreas, which play a vital role in regulating the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. Insulin is a protein made up of 51 amino acids and is produced and secreted by the beta cells in the islets of Langerhans.
Insulin targets liver cells, muscle cells, and fat cells and has several effects on these cells. It stimulates liver and muscle cells to store glucose as glycogen and inhibits glucose production by the liver and kidneys. It also stimulates fat cells to make fat from fatty acids and glycerol and stimulates liver and muscle cells to make protein from amino acids.
Recently, researchers used laboratory-engineered human pancreatic cells to treat type 1 diabetes in mice. The study showed that these cells could secrete insulin and stabilize blood sugar. However, there are still several barriers to using this method in humans, including nerves and the source of blood tissue.
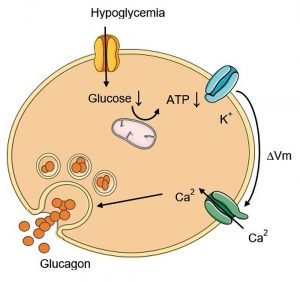
Glucagon is a hormone that is secreted by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans Islands alpha cells when blood glucose levels drop, leading to hypoglycemia. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include chills, dizziness, and difficulty speaking, and can be treated by consuming a snack or drink such as juice, soft drinks, or candy. On the other hand, hyperglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels are high and is characterized by frequent urination and excessive thirst.
Glucagon, unlike insulin, raises blood sugar levels and is a large polypeptide made up of 29 amino acids with a molecular weight of 3485. It is produced as a precursor and undergoes changes and transformations to become an adult hormone. When blood glucose levels drop, the pancreas produces glucagon, which signals the liver cells and muscles to change glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream to provide energy for the cells.
The pancreas is responsible for releasing both insulin and glucagon. When the secretion of either hormone is low, it can lead to severe damage to the body. The levels of insulin and glucagon in the blood interact with each other, with an increase in one leading to a decrease in the other, and vice versa. For example, when we eat, the digestive system is stimulated, leading to the secretion of insulin by beta cells and the blocking of glucagon secretion by alpha cells.
However, a few hours after eating, the body needs to maintain its energy levels, and this is achieved by the stimulation of alpha cells to produce glucagon, which helps to return glucose levels to normal. The balance and interaction between insulin and glucagon ensure that we have enough energy throughout the day and can engage in various activities without having to eat continuously.

The Hemoglobin test, also known as HbA1C, Glycated Hb, or Glycosylated HB, is used to monitor and assess diabetes. It examines blood sugar levels from 2 to 3 months ago by looking at different types of hemoglobin, where 95% to 97% are typically called A1. When sugar binds to this hemoglobin type, it becomes glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and the higher the sugar concentration, the higher the level of HbA1c. This connection lasts until the end of the red blood cell’s life, which is about 120 days or three months. While many patients measure their blood sugar at home, doctors need to monitor long-term control of the disease.
The A1C test provides doctors with a glimpse of blood sugar levels over the previous 120 days, equivalent to the lifespan of a red blood cell. Doctors use the A1C test results to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment plan prescribed to patients. This test should be conducted at least twice a year, and doctors may perform it more frequently for patients who have difficulty controlling their blood sugar or recently changed their treatment plan.
Self-monitoring using a blood glucose meter is crucial for patients to control their blood sugar, particularly for those who inject insulin or have uncontrolled blood sugar. There are many benefits to controlling blood sugar, including determining the effect of food consumption on blood sugar and adjusting insulin intake during activity or illness. Blood glucose meters require a small drop of blood to be placed on a disposable tape, which is then inserted into the device to measure blood glucose levels. Some devices measure blood sugar using electric current, while others use light spectrum reflection and light reflection.
Blood tests must be given to diagnose diabetes, and blood glucose monitors should not be used for diagnosis. Regular fasting blood sugar levels for individuals without diabetes should be less than 100 mg/dl. If a person’s blood sugar level is more than 126 mg/dl, and this rate is repeated once more, they have diabetes. Individuals with symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination, binge drinking, and weight loss, and have a blood sugar level of above 200 mg/dl at any time, have diabetes. A person with a fasting blood sugar level between 100 and 126 mg/dl is prone to diabetes.
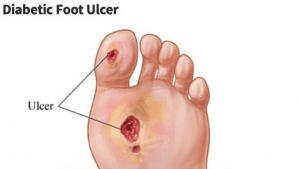
One of the complications caused by diabetes is chronic and non-healing wounds that typically develop on the soles of patients’ feet, which is known as diabetic foot. Two major problems contribute to foot issues in people with diabetes: peripheral nerve disorders and reduced blood flow to the limbs. The feet are the farthest part of the body from the heart, and they receive less blood than other tissues in the body, especially in cold weather. Although diabetes eventually reduces blood flow throughout the body, the foot is affected more than other body parts. This can cause wounds that usually heal quickly in other people to remain open in diabetic patients because wound healing requires nutrients and oxygen that reach the tissues through the blood. Also, germs infect the wound due to the reduced blood flow, and the immune defenses are lowered since white blood cells are less likely to reach the wound site.
Furthermore, diabetes impairs peripheral nerve function, causing a loss of sensation in the feet, making the skin dry and prone to cracks. Additionally, patients are less aware of environmental damage due to decreased sensation. For example, they may accidentally place their foot on a hot object without noticing it, leading to burns. This condition also lowers the immune system in general, contributing to spreading the infection to the wound and delaying its healing.

Diabetes treatment:
Chronic effects of diabetes mellitus can be prevented or delayed through the regulation of glucose, fat, and blood pressure. Diet, medication, and physical activity are the three primary methods used to control the disease. Exercise is an effective means of controlling diabetes and its adverse side effects. Endurance, resistance, and combined sports are recommended, as they increase insulin sensitivity, Glut4 muscle, and blood flow while decreasing hepatic glucose production and normalizing blood lipids. One session of aerobic exercise is capable of increasing insulin sensitivity for 24 to 72 hours. Long-term resistance training increases glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity while also building skeletal muscle mass and increasing glycogen stores. However, when prescribing exercise for diabetics, one must consider the complications of the disease, the level of disability, and any orthopedic limitations. Exercise has the potential to reduce fasting blood sugar and hemoglobin A1c levels, indicating long-term blood sugar status. The prevalence of diabetes worldwide is estimated to reach 21% by 2050, making it the most common metabolic disease.


