Who needs knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery or arthroplasty, in which the damaged bones and cartilage are removed and replaced with an artificial joint.
Everything about knee replacement surgery or arthroplasty
Knee surgery is called arthroplasty, which helps relieve pain and restore function to damaged parts of the knee joint. In this process, the bone and cartilage’s damaged parts are removed from the thigh and replaced with an artificial joint made of high-quality metal, plastic, and polymer. To determine if this surgery is right for you, you should see an orthopedic surgeon check your age, weight, activity level, knee size and shape, and overall health.
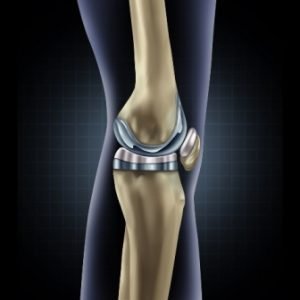
Arthroplasty means the repair of a joint through surgery that uses artificial components.
When specific cartilage in the body is damaged or destroyed, it becomes painful and cannot be moved, and as a result, the bones may rub against each other and break each other, in which case the patient is in a lot of pain. He feels in the knee joint and can not move his knee well. In this situation, the standing position and his three joints are photographed to examine the ankle and pelvis joint, then the patient’s knee is photographed from the side. Becomes.
The main reasons for knee joint surgery or arthroplasty
Osteoporosis depends on a person’s age, which can sometimes lead to rupture and knee joint loss. It can also affect patients over the age of 50, which also occurs in younger people. Osteoporosis occurs due to inflammation, fractures, and gradual loss of articular cartilage. As cartilage breaks down over time, the bones wear away from each other, causing the bones to thicken often and cause pain. (Osteoporosis: Symptoms And Treatment Of Osteoporosis)
One of the most important causes of knee pain in people over 40 is knee joint osteoarthritis, which is the most common destructive disease among the body’s joints. The joints become dry and painful in osteoarthritis. Sometimes the terrible pain of osteoarthritis causes the patient not to use his joint. As a result, the joint’s muscles become weak and make it difficult for the patient to move the joint. The cartilage around the joints is affected by this disease. The slippery texture of these cartilages, located at the end of the bones, allows the joint bones to slide on top of each other. Osteoarthritis causes the top layer of cartilage around the joints to break down and wear out. As a result, the bones rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion of the joint.
Osteoarthritis
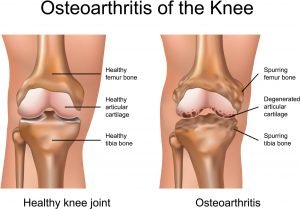
This type of osteoarthritis is caused by aging and high activity. But it can also occur at a young age. In this disease, the cartilage that runs through the bones is destroyed, causing wear and tear on the knee and causing pain. Joint damage from osteoarthritis or trauma can cause problems with elementary activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and even sitting or lying down.
Osteoarthritis caused by the lesion
One of the most acute and severe diseases of the knee is osteoarthritis caused by a lesion. Over time, fractures of the bones around the knee and stretching of the ligaments damage the knee’s cartilage. As a result, knee pain reduces its function.
rheumatism
Rheumatism is an inflammatory disease in which the membrane around the knee becomes thick and inflamed, and this chronic inflammation damages the cartilage, resulting in burning and stiffness.
Injury
This type of pain occurs due to severe injury to the knee. This can affect the knee’s cartilage when the bones around the knee break or the ligament between them break.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
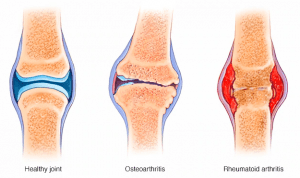
A lot of fluid is secreted in rheumatoid arthritis due to the synovial layer’s growth and inflammation. Inflammation of the synovial layer gradually leads to the destruction and damage of the knee’s articular cartilage, which causes pain and limited movement in the knee joint.
Who needs knee joint surgery?
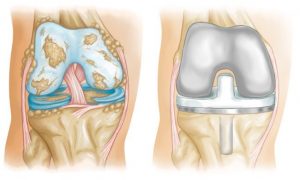
This surgery is suitable for people with the following conditions:
- People who experience severe pain or stiffness in the knee prevent them from doing daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, getting in and out of a car, climbing out of a chair, and so on Prevents.
- Regular but persistent knee pain may also be felt while sleeping and resting. Chronic inflammation of the knee and swelling in these cases will not go away after taking medicine and resting.
- Deformity or deformity of the knee, which is quite evident from its appearance, which sometimes leads to braces or crossed legs
- Depression is the result of an inability to perform daily activities due to knee pain.
- Ineffective treatment options other than surgery in people with knee joint pain
Types of knee replacement surgeries
Knee dislocation can be general or lateral.
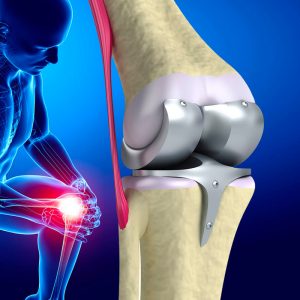
Total knee joint displacement or TKR:
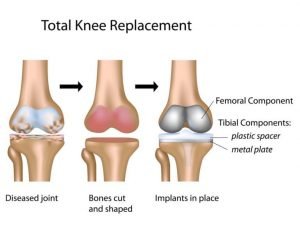
In this surgery, both sides of the knee joint are moved. This process is quite common. The surgery takes about 1 to 3 hours, after which the pain subsides, but the scar tissue around the surgical site may prevent the person from bending or moving their knees quickly.
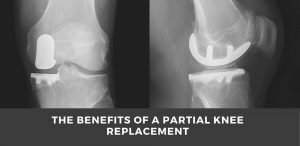
Lateral knee joint displacement or PKR:
This type of displacement occurs only on one side of the knee joint. Fewer bones are removed, so the incision is shorter and takes less time than a total displacement.
Lateral surgery is suitable for those whose only part of the knee is injured. Corrective movements and exercises begin immediately after surgery, and blood loss is less in this surgery, thus reducing the risk of infection and blood clots.
Risks and side effects
Joint dislocation surgery is also associated with risks, including:
- Infection
- Blood clots in the arteries of the legs
- heart attack
- Nerve damage
- Allergic reactions
- Artificial joint fracture
Symptoms of infection also include the following:
- Fever above 100 degrees Fahrenheit or 37.8 degrees Celsius
- To shiver
- Discharge in the surgical department
- Increased redness, pain, and inflammation in the knee surgery area
When a person becomes infected after surgery, the prosthetic joint must be removed during another operation and the bacteria killed by antibiotics. After the infection is cleared, another operation is performed to reposition the artificial knee joint.
Elimination of the artificial knee joint
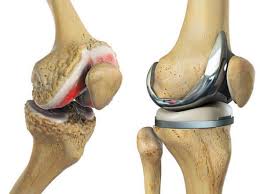
Another danger is artificial joint damage, which can happen to even the strongest artificial joints—the risk of joint damage increases when pressing on the joint and lifting heavy objects and high-pressure activities.
Before the surgical procedure
This surgery requires anesthesia. It does not matter if your anesthesia is general or local; sometimes, it is up to you to choose. You will also be given antibiotics before, after, and during surgery to prevent infection, and your knee nerve may also be anesthetized, which will gradually go away during the surgery.
During the surgical procedure
Place your knee in a bent position to expose all joint surfaces. After an incision of about 15 to 25 cm in length, the surgeon moves the knee’s patella, cuts the joint’s damaged surface, and then attaches the artificial joint pieces to the knee. Before suturing, he bends and bends the knee and tests it for proper operation. This surgery takes about two hours.
After arthroplasty surgery
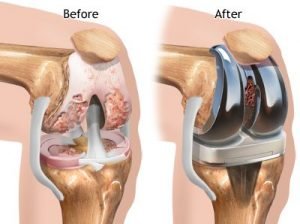
After the surgery, you will be taken to the recovery room for one to two hours; then, you will be admitted to the ward, where you can stay for a few days. Medications prescribed by your doctor can also help you control your pain.
When you are in the hospital, you are encouraged to shake your ankles and soles to increase blood flow to the muscles, prevent blood clots, and swelling and blood thinners and foot compresses. They also prescribe breathing exercises that will gradually increase your activity level.
The therapist will show you how to practice the new knee the day after surgery. He also prescribes home remedies after you leave the hospital.
Post-operative care
Like any surgery, the patient must prevent the wound from becoming infected. For this reason, it is better to bandage the wound once every three days. While taking a bath, the patient should apply soap and soap to the stitches, and after bathing, dry the wound with a hairdryer and bandage it again.
If allowed by the doctor, the patient should walk without a cane and walker and do it if physiotherapy is prescribed.
Physiotherapy after surgery

Physiotherapy has many benefits for patients, as some post-operative patients do not know which activities are right. Physiotherapy guides them.
Physiotherapy devices such as ultrasound, laser, and CPM machine, which is placed under the patient’s knee, without bending the patient, the knee bends and straightens with the degrees adjusted by the doctor.
Benefits of Knee Replacement
The most crucial benefit of this operation is that the patient’s pain disappears, and the brace and cross shape of the legs are eliminated. Most patients who suffer from knee pain cannot sit and walk properly and perform their activities well after this operation. The ability to perform personal and daily activities is another advantage of this practice. The sounds produced by the knee are eliminated when the knee is walking and dislocated.
Disadvantages of knee replacement surgery
One of the reasons for being overweight is inactivity and walking. The joint inserted inside the knee can only bear up to 110 kg, so patients are asked to lose weight and keep it low until, After the operation, the joint should not go in and should not be pushed back.
The disadvantages of this operation are dislocation, rejection, or infection. At the diagnosis of infection, the joint is removed by the doctor, and the infectious disease specialist prescribes the relevant antibiotic to the patient to eliminate the infection.
The reason for some unsuccessful knee replacement operations
Knee replacement surgery is an effective procedure that requires consideration. Most people who have this surgery should take anticoagulants such as warfarin and aspirin to not clot after the operation. One of the most common causes of death after knee replacement surgery is the formation of a blood clot, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke if it moves to the heart or brain, and if it goes to the lungs, it can lead to pulmonary embolism and death. Of course, this can also happen in other surgeries.
Cost of knee replacement
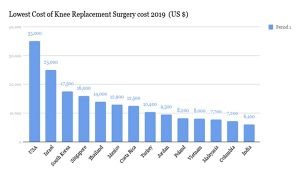
In practice, knee replacement requires a plastic joint, determined by the plastic knee joint’s price and cost by a specialist doctor. Hospital costs are added to hospitalization costs depending on whether the patient is admitted to the ICU or CCU. In public hospitals, the patient does not incur this additional cost.
Surgical results

For many people, knee joint surgery relieves pain, improves mobility, and improves life quality, and most of these joints last up to 15 years.
Three to six weeks after surgery, you can gradually return to your daily activities such as shopping. Driving is also suitable after three weeks if you are entirely able to bend your knees or get in the car. Of course, if you have enough control over keeping the muscles.
After recovery, it is better to do walking, swimming, cycling, and golf. Of course, avoid strenuous activities such as tennis, skiing, skipping rope, jumping, and talking to your doctor about restrictions.