What is the normal blood oxygen level?
The amount of oxygen in the blood is known as blood oxygen levels. Almost all oxygen in the body is carried by red blood cells, which collect it from the lungs and transport it throughout the body.
All cells in the body receive adequate oxygen from the blood, which is strictly regulated by the body. Blood oxygen levels indicate how effectively the body distributes oxygen from the lungs to the cells and can affect health.
A person’s health can be affected by both normal and low levels of oxygen in the blood.
Blood oxygen levels should range from 75 to 100 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). If the arterial blood gas (ABG) test results indicate that the oxygen level is less than 60 mm Hg, it is considered low. Supplemental oxygen may be required for these individuals.
Hypoxemia (hypoxia) is characterized by low blood oxygen levels compared to the normal level of oxygen in the body. When this condition occurs, the body has difficulty delivering oxygen to all of its cells, tissues, and organs.
Saturation of oxygen:
The oxygen saturation of a person refers to how much oxygen is in their blood. Medical professionals use pulse oximeters for rapid testing or continuous monitoring. An earlobe or fingertip can be attached to it.
A healthy oxygen saturation level is between 95% and 100%. When a person’s oxygen saturation level drops below this level, he or she may experience symptoms of hypoxia, including difficulty breathing and dizziness.
What is the best way to measure blood oxygen levels?
The most reliable way to measure blood oxygen levels is with an ABG test. For this test, blood is drawn from an artery, usually in the wrist. The procedure is very precise, but it can be painful.
Hospitals perform ABG tests. A pulse oximeter can also be used to measure blood oxygen levels at home.
What is the purpose of a pulse oximeter?
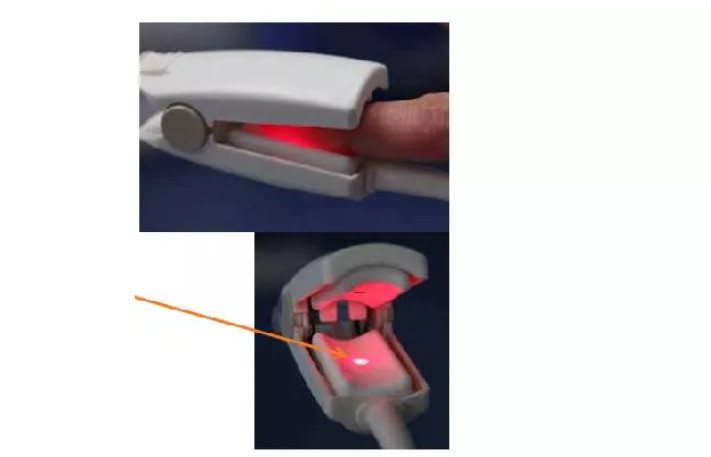
The pulse oximeter consists of two sensors (or probes) and a display. When the probe is placed on the finger, it detects blood flow inside the finger. As a pulse wave, the display shows the current.
The pulse has been detected if a pulse wave is present. In this figure, the patient’s pulse rate is 72 beats per minute and his oxygen saturation level is 98%. Heart rate is shown as pulse rate.
Two types of red light are emitted by pulse oximeter probes (finger or ear) using light emitting diodes (LEDs). After the light has passed through the tissue, a sensor receives the other side. Oximeters can measure the percentage of arterial blood oxygen saturation in peripheral blood by determining what light is coming from hemoglobin in pulsating (arterial) blood.
Oximeters measure oxygen levels in the blood and how much light is absorbed by the blood. Infrared and red lights are emitted by a pulse oximeter at the fingertip or earlobe. Blood that is oxygenated absorbs more infrared light and transmits more red light. When blood is oxygenated, it absorbs more red light and allows more infrared light to pass through. If you do not have enough oxygen in your blood, your blood cells will appear blue.
The pulse oximeter test is easier, faster, and less painful than the ABG test, but it is not as accurate. Results may be affected by several factors, including:
Fingers that are dirty
Light in the environment
Color of the skin: dark
Polish for nails
Organs with poor blood flow
Low blood oxygen levels can cause a variety of symptoms
The following symptoms can occur as a result of low blood oxygen levels:
Breathing problems
Having a headache
Feeling restless
Dizziness
Breathing quickly
Pain in the chest
Feeling confused
Hypertension
Coordination problems
Disorders of the vision
Happiness
Heart rate that is fast
There is not enough oxygen in the air
All cells and tissues cannot receive oxygen from the lungs
It is impossible for blood to circulate in the lungs, collecting oxygen and transporting it throughout the body.
Hypoxia can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, including:
Insufficiency of air
Congenital heart defects, including heart disease
Altitude
The anemia
Diseases of the interstitial lungs
Asthma
ARDS stands for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.
Infection with pneumonia
Obstruction of the pulmonary arteries
Lung fibrosis, ulceration, or injury
Collapse of the lungs due to the presence of air or gas in the chest
Inflammation of the lungs caused by excess fluid
Shortness of breath during sleep caused by sleep apnea
Medications, such as narcotics and painkillers, can cause sleep disorders
When should you call a doctor if you have decreased blood oxygen?
Sudden and severe shortness of breath
Even while resting, sudden
Exercise-induced shortness of breath that is severe and sudden
A sudden feeling of suffocation or shortness of breath when they wake up
Shortness of breath, coughing, rapid heartbeat, and fluid retention may occur at high altitudes
Blood oxygenation strategies and treatments
Oxygen can be used to treat low blood oxygen levels. In addition to oxygen therapy in the office, doctors can prescribe home oxygen therapy (HOT) to their patients.
It is possible to deliver and monitor HOT with a variety of devices, but some require a prescription.
In addition to improving general health and quality of life, people can modify their lifestyle in order to reduce the symptoms of low oxygen levels. Here are some examples:
Don’t smoke
Secondhand smoke exposure
Eat a diet rich in fruits, whole grains, lean protein, and vegetables
Exercise on a regular basis
Blood oxygen levels are generally improved by treating hypoxia’s underlying conditions. COPD and COvid 19 are chronic lung diseases that require regular monitoring of blood oxygen levels. Those with low blood oxygen can improve their diet and exercise habits, for example. An individual can increase their oxygen saturation level with these, as well as oxygen therapy.
In a nutshell:
Oxygen levels in the body are determined by a person’s blood oxygen level. Blood oxygen levels can be measured with pulse oximeters. Low pulse oximeter readings are considered low by doctors.
Low blood oxygen levels can be caused by asthma, anemia, and covitis. A doctor may also recommend oxygen therapy or lifestyle changes in addition to treating the underlying cause.


