Redness in one eye without pain + video
Redness in one eye without pain : The human eye, a complex and sensitive organ, frequently communicates its well-being or distress through noticeable changes in appearance. One such change that is often observed but not always understood is redness in just one eye, without accompanying pain. This phenomenon, while sometimes alarming, can arise due to a myriad of reasons, some benign and others requiring medical attention. This essay delves into the possible causes, underlying conditions, and their implications.
How to Get Rid of Red Eyes :
Redness in one eye without pain :
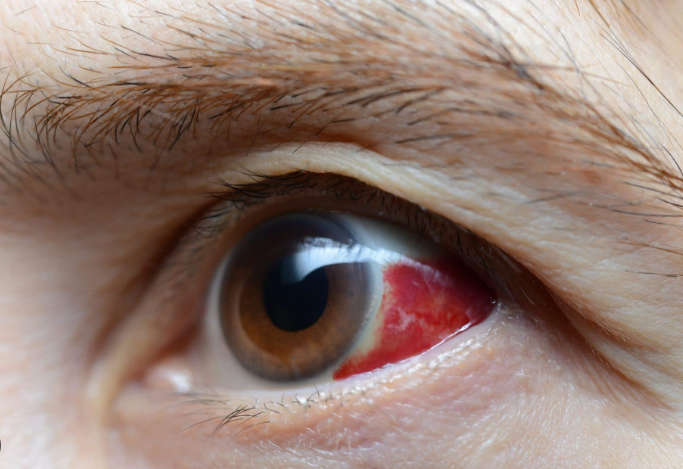
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage: This is one of the most common causes of redness in one eye without pain. It refers to a broken blood vessel in the eye. Although the eye may appear intensely red or bloody, this condition is generally harmless. A subconjunctival hemorrhage can result from a strong sneeze, cough, or minor trauma to the eye. Aging, diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain medications can make one more prone to this.
How to get rid of red eyes FAST :
Foreign Body: Sometimes, a small particle such as dust, sand, or an eyelash can get trapped in the eye. While it may not always cause pain, the eye’s natural response is to increase blood flow to the area, resulting in redness. The eye might also water excessively.
Dry Eyes: Insufficient tear production or poor tear quality can lead to dry eyes. This lack of lubrication can make the eye appear red. Factors like prolonged screen time, certain medications, and aging can contribute to dry eyes.
Contact Lens Wear: Extended or inappropriate use of contact lenses can lead to redness in one or both eyes. This can be due to reduced oxygen supply to the cornea, accumulation of debris under the lens, or minor injuries while inserting or removing the lens.
Iritis or Uveitis: Iritis refers to the inflammation of the iris, the colored part of the eye, while uveitis is the inflammation of the middle layer of the eye. Both conditions can lead to redness in one eye without pain, especially in the early stages.
Episcleritis: This condition involves the inflammation of the episclera, a thin layer of tissue covering the white part of the eye. It often appears as a localized red or pink area and may not always be painful.
Underlying Conditions
While the aforementioned causes directly relate to the eye, some systemic conditions can manifest as redness in one eye. These include:
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or Sjogren’s syndrome can cause eye inflammation and redness.
- Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus: A reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus in the ophthalmic nerve can lead to this condition. While it can be painful, initial stages might just show redness in one eye.
- High Blood Pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can lead to damages in the blood vessels of the retina, causing redness in the eye.
- Blepharitis: This involves the inflammation of the eyelid margins, often due to bacterial infections or skin conditions like dandruff or rosacea. One eye may become redder than the other, depending on the severity and location of the inflammation.
Implications and Management
A sudden or persistent change in the appearance of the eye should never be ignored. Even if there is no pain, redness in one eye can indicate an underlying issue that needs attention. Here are some general guidelines:
- Prompt Medical Consultation: If the redness is accompanied by other symptoms like visual disturbances, excessive tearing, or sensitivity to light, it is crucial to see an ophthalmologist immediately.
- Regular Eye Check-ups: Routine eye exams can detect issues before they become symptomatic. Individuals with a family history of eye diseases, or those with systemic conditions like diabetes, should be especially diligent.
- Protective Measures: Wearing protective eyewear during activities that pose a risk of eye injury, and ensuring good hygiene, especially for contact lens wearers, can prevent many causes of redness.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Limiting screen time, ensuring adequate lighting while reading, and taking breaks during prolonged visual tasks can reduce the strain on the eyes and prevent redness.
In conclusion, the eyes are not just the windows to the soul but also indicators of overall health. While painless redness in one eye might seem trivial, it can be a sign of a deeper issue or an early symptom of a developing condition. Recognizing the potential causes and understanding the importance of timely intervention can go a long way in preserving the health and function of this vital organ.


