Kidney stones and methods of prevention and treatment
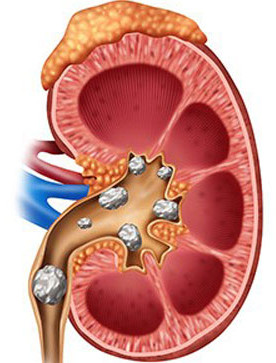
A kidney stone is a hard deposit of acidic salts inside the kidney that causes pain in the lower back and flanks, which will differ depending on the type of stone. Various causes of kidney stones, such as family history or improper nutrition, are treated based on the type of stone and the patient’s condition. Stones form in the kidneys as a result of the buildup of acidic salts and salts.
In most cases, kidney stones are caused by concentrated urine allowing minerals to crystallize and stick together. They are usually painful to move and pass. In most cases, the pain starts in the side or back below the ribs and then moves to the lower abdomen or pelvis. As the stone enters the urinary tract, the severity of the pain changes; continue to research causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods, and kidney stone treatment.
types of kidney stones
This type of stone occurs in people who are dehydrated or dehydrated; such as those on high-protein diets or who have gout. Uric acid stones are also caused by genetic factors and deficiencies in the tissues that make up the blood.
Cystine stones: These types of stones make up a small percentage and are caused by inherited deficiencies. Cystinuria results from the excretion of high levels of some amino acids due to this inherited deficiency.
Calcium stones: Most kidney stones are calcium stones. Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and chocolate contain high levels of oxalate. Oxalate is also produced by the liver. Dietary factors, high vitamin D levels, bowel bypass surgery, and numerous other metabolic disorders may increase calcium or oxalate levels in the urine. Calcium phosphate stones can also occur.
Stones can form as a result of an infection, such as a urinary tract infection. Such stones can form and proliferate.
signs of kidney stones
When kidney stones enter the urethra, they cause symptoms. The urethra is the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder. During this time, the following symptoms appear:
kidney stone pain
Pink, red, or brown urine
Vomiting and nausea
There is severe pain in the flanks and lower back, just below the ribs
There is also widespread pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis
Constant urge to urinate
Fever and chills when infected
Tests for kidney stones
A doctor who suspects kidney stones will order tests and procedures to make a definitive diagnosis, including:
Tests of the blood show an increase in calcium or a high level of uric acid.
A 24-hour urine test will show large amounts of salts in your urine if you have kidney stones.
Visual tests: Visual tests reveal any stones in your urinary tract. In most cases, imaging tests include a CT scan and, in some cases, X-rays.
A strainer is used when urinating to collect excreted stones. These stones are then collected for laboratory testing.
kidney stones treatment
avoiding certain foods :
Among the best home remedies for kidney stones, this is at the top of the list. What should you do? Avoid chocolate, wheat flour, and nuts.
The easiest way to get rid of kidney stones is to drink water.
Drink lots of water :
Water is one of the best and simplest home remedies for kidney stones. When you are well hydrated, your urine should be clear and yellow; As a general rule, drink half a pound of water every day. If you weigh 140 pounds, you should try to drink 70 ounces of water a day; as you work harder, increase your water intake throughout the day.
The following are some benefits of pomegranate juice :
Another important medicine for kidney stones is pomegranate juice. When this illness increases, double the amount of pomegranate juice consumed. Pomegranate juice helps prevent this illness and eliminates calcium, sodium, and uric acid (that cause this illness).
Tea made from nettle leaves :
Nettle leaf tea can be added to the list of home remedies for treating this illness. Mix one-half cup of nettle leaf tea with two cups of water, then wait a few minutes for the tea to boil, then strain and remove the leaves. Drink this drink up to three times a day.
Diet high in fiber :
As a primary method of preventing kidney stones, a high-fiber diet is also recommended. Incorporate high-fiber foods into your daily diet.
Prevention of kidney stones

Watermelon :
Another delicious home remedy for this illness is watermelon. If you suffer from kidney stones, eat two to three pieces of watermelon each day. In general, include watermelon and melon in your diet. Make them a regular part of your diet. Eat plenty of fruit salads that also contain watermelon.
vitamin A :
Include a medium number of carrots in your diet on a daily basis to prevent kidney stones without vitamin A. You can also add celery to make it more effective. Sweet potatoes, broccoli, and pumpkin are also good sources of vitamin A.
Lemon juice
Add a tablespoon of olive oil to lemon juice, and drink this mixture two to three times a day.

Vinegar made from apple :
Imagine you are searching for one of the best home remedies to cure this illness. You can drink the mixture several times a day by adding two tablespoons of apple cider vinegar in 8 ounces of warm water and adding honey to taste.
Basil :
Basil is another remedy for kidney stones. Drink a teaspoon of basil every 4 to 6 hours or chew 2 to 3 raw basil leaves several times a day to remove stones.
Citrus oil essential oil :
Citrus essential oil can also be useful as a home remedy for this illness. Add 2 to 3 drops of lemon, orange, or grapefruit to water and drink it twice a day.
magnesium :
Magnesium is another home remedy for kidney stones. Add magnesium-rich foods to your diet, and take 250 mg of magnesium twice a day.
Dandelion root :
Contrary to popular belief, weed is one of the most important remedies for this disease. Add a tablespoon of chopped dandelion root to a cup of water and simmer for five minutes. Remove the roots and drink them. You may also add a little honey. Drink this drink several times throughout the day. You can also take 250 grams of dandelion root supplement daily.
Aloe vera juice:
This is not the last time we have mentioned this plant in our list of home remedies; this plant is also useful for removing kidney stones. Each day, you can drink a quarter cup of aloe vera juice alone or mixed with warm water.
Factors that increase the risk of kidney stones include
family history
If someone in your family has kidney stones, you are more likely to develop stones. If you have had one or more kidney stones before, you are at risk of getting them again.
Dehydrated
Not drinking enough water can increase the risk of developing kidney stones. People who live in hot climates or sweat a lot may be at higher risk than others.
Special diet
Having a diet high in protein, salt, and sugar may increase the risk of some types of kidney stones. Too much salt in your diet increases the amount of calcium and the kidneys and significantly increases the risk of developing kidney stones.
Obesity
High body mass index, high waist size, and weight gain are associated with an increased risk of kidney stones.
Gastrointestinal diseases and surgery
Gastric bypass surgery, an inflammatory bowel disease, can cause changes in the digestive process that affect the absorption of calcium and water and increase the number of stones in the urine.
Diagnosis of kidney stones
If your doctor suspects you have kidney stones, you should have the following tests and diagnostic tests:
blood test
Blood tests may show large amounts of calcium or urea acid in the blood. Blood test results help monitor kidney health and other diseases.
Clinical urine tests
A urine test collected over 24 hours may indicate that you have consumed too much stone formation minerals.
For this test, your doctor may ask you to have two urine tests for two consecutive days.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging from inside the urinary tract may show kidney stones.
An option is to use a plain X-ray, which may not show small kidney stones.
The second option is high-speed computed tomography (CT), which shows even small stones.
Medical treatments
Your doctor may prescribe medication to help eliminate kidney stones. These drugs, known as alpha-blockers, relax muscles, and reduce pain.
kidney stone pain relief
some kidney stones can not be treated with the usual methods due to their large size and bleeding danger, or even urinary tract infection, so that you may need more extensive treatment in these cases.
Treatments may include the following:
Use sound waves to break the stones. Depending on their size and location, your doctor may recommend a Lithotripsy procedure for some kidney stones.
This treatment causes the stones to break into small pieces to pass through the urethra. This process takes about 45 to 60 minutes and can cause moderate pain, so you may be taking sedatives or anesthetics to relax.
ESWL can cause blood in the urine, bruising on the back or abdomen, and bleeding around the kidneys and other organs.
Use a scope to remove stones:
To remove a smaller stone in the bladder or kidney, your doctor can use a camera-equipped urethroscopy to pass through the bladder canal. When a stone is seen, special tools can remove the stone or crush it to pass through the urine. You may need general or local anesthesia during this procedure.
Parathyroid gland surgery:
The bladder glands make some calcium phosphate stones. When these glands produce too much parathyroid hormone, the amount of calcium can rise too high, and kidney stones may form.
Hyperparathyroidism occurs when a small, benign tumor forms in one of your digestive glands. Stopping the growth of the gland prevents the formation of kidney stones. Or your doctor may recommend treatment that causes the parathyroid gland to produce more hormones.
Kidney disease in women
With unhealthy lifestyles and eating habits, kidney disease is no longer uncommon. Around 850,000 people die each year from kidney disease and other urinary tract problems, according to the World Health Organization.
A chronic disease, also known as chronic failure, is a factor in the decline of kidney function over several months or years. An individual with chronic kidney disease has a glomerular filtration rate of less than 60 ml / min or 1.73 m2 in three months or more.
Each stage of a woman’s life affects her health differently. Women of childbearing age have different kidney problems from men, for example. High blood pressure and blood clots can aggravate the condition. For women with insufficiency taking birth control pills, their risk increases if they have significant problems; even women without kidney disease can become pregnant. The risk of childbirth is increased by preeclampsia and high blood pressure. High blood pressure and preeclampsia during pregnancy can lead to this organ’s insufficiency and increased risk of disease as we age.
Every year, more than 10 million people are hospitalized for urinary tract infections. Germs can spread to this part of the body and cause a more severe type of infection than pyelonephritis if left untreated. Pregnancy increases the risk of urinary and renal infections, which have become a widespread problem.
A number of lifestyle habits damage the kidneys and reduce their ability to purify blood waste, resulting in chronic kidney disease. In the body, waste accumulates, and if the kidneys cannot filter it, it can lead to many complications.

Common kidney diseases in women
Lupus nephritis (LN) :
Lupus nephritis is an autoimmune disease that causes damage to this organ. Immune system attacks body cells and tissues. Lupus-associated kidney disease may worsen over time and lead to kidney failure. Women are more likely to suffer from this condition than men, and it usually occurs during the reproductive years. Nine out of ten people with SLE are female.
Pyelonephritis (kidney infection):
Pyelonephritis is an infection of the lower urinary tract caused by bacteria. Left untreated, it can spread to the kidneys. Infections of the kidneys can be dangerous. Due to anatomical factors, urinary tract infections are more common in women and girls.
Common symptoms of kidney disease in women
Women are more likely to suffer from urinary tract infections because their urethra is shorter and closer to the anus. Therefore, bacteria are more likely to enter the urinary tract. Some older women with kidney infections may not have urinary tract infection symptoms and may not see a doctor. If not treated in time, this infection can cause permanent kidney damage. If not treated in time, this infection can cause:
Symptoms of kidney infections include fever and sometimes fever with chills. Fever starts suddenly and reaches above 101 degrees Fahrenheit in these people. Chronic kidney infections may not cause a fever or may cause a periodic fever.
In women, kidney infection can cause pain on both sides of the spine and on the same side of the body where the kidneys are infected. A severe infection in this organ is characterized by abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Symptoms of kidney infection include urinary changes and the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Urge to urinate immediately
- A burning sensation when urinating
- dark urine
- Blood in the urine or pink or rust-colored urine
Infections of the kidney and urinary tract, if not diagnosed and treated in time, can spread to the bloodstream and cause sepsis.
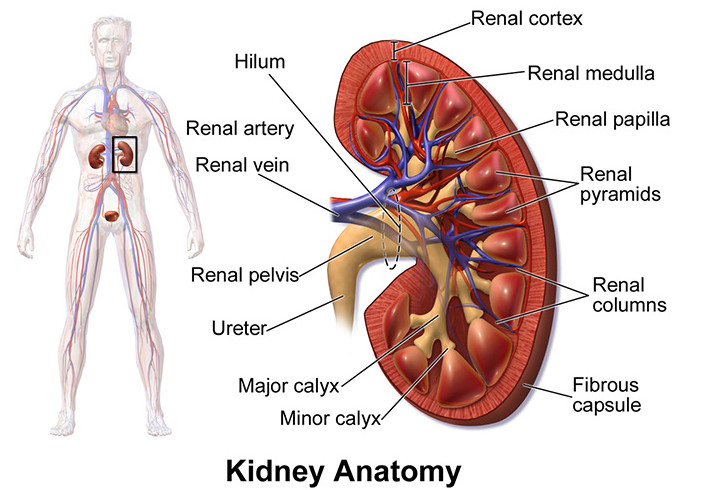
Causes of chronic kidney disease
48% of men and 63% of women are obese in the abdominal area. Obese people are more likely to develop kidney disease than people of normal weight. Obesity accelerates the progression of kidney disease and its complications.
40-60% of chronic kidney disease is caused by diabetes and high blood pressure. Almost 75% of the population with an average or low body mass index has hypertension.
Arsenic, cadmium, fluoride, etc., are thought to pose a threat to kidney histology and chronic interstitial nephritis. In its early stages, chronic kidney disease is silent and asymptomatic. Patients with severe kidney disease:
- Weakness and fatigue
- Pain when urinating
- Inflation
- Frequent urination
- backache
- Anorexia
- Vomiting or nausea
- Cause of kidney disease
- Method of diagnosis of kidney disease in men and women
The problem occurs when examinations are delayed. Diabetes and high blood pressure are caused by unhealthy lifestyles. Changing your lifestyle and eating habits early can prevent kidney damage.
The following tests should be performed to screen and diagnose kidney function:
1- The presence of several markers in the blood indicates kidney function.
2- A urine test measures kidney clearance by comparing urine and blood markers.
3- Estimation of glomerular filtration: In order to determine the amount of glomerular filtration in the kidneys, a formula must be used that considers creatinine and serum levels, as well as toxin, sex, and race.
4- Imaging tests: Ultrasonic waves are used in kidney ultrasound to analyze the shape, size and function of this organ, which often detects damage to this organ or a change in filtration capacity.
prevention
Although we can’t do much about external damage to the kidneys and aging, many other major risk factors that contribute to kidney disease can be prevented.
As you age, regular exercise can help reduce the risk of kidney disease.
Blood pressure should be controlled to prevent kidney failure.
Diabetes patients should eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and control their blood sugar levels.
Limit salt intake.

Kidney infection during pregnancy; Causes, treatments, and preventive measures
Pregnancy is associated with health problems, but not all of them can be ignored, such as kidney infections, which need immediate attention. The changes in the urinary tract structure during pregnancy reduce urine flow, resulting in a bacterial infection in the lower urinary tract that spreads to the bladder, then one or both kidneys.
What causes kidney infection during pregnancy ?
Infection of the kidneys, or inflammation of the pelvis and kidneys, occurs when the infection enters the upper urinary tract. This causes inflammation of the kidney tissue and pelvis. Bacteria that enters the bladder and kidneys through the urethra often cause infection. Klebsiella pneumoniae is another bacterium that can cause a urinary tract infection. The most common cause of infection is a change in the urinary tract, such as an enlarged kidney or a compressed urethra and bladder.
Kidney enlargement:
During pregnancy, the hormone progesterone releases a high concentration, which delays the urinary tract and reduces urine flow. As a result, it accumulates in the bladder, causing the kidneys to enlarge and giving the bacteria time to multiply and cause infection.
Bladder compression:
As the uterus grows, it puts pressure on the urethra and bladder and restricts urine flow. In women, the infection spreads much more quickly than in men, because their urethra is shorter and closer to the anus. Therefore, bacteria pass from the stool in the anus to the urinary tract.
What are the symptoms of kidney infection during pregnancy?
Infections of this organ can be classified as acute or acute pelvic infections, each of which has different symptoms.
Symptoms of acute pelvic infection include:
- Backache, fever
- Decreased appetite
- Pregnant women who have been pregnant for more than 16 weeks suffer from severe abdominal pain.
- Fever accompanied by a sudden rise in body temperature.
- Concentrated urine with pus.
- Vomit.
- Kidney sensitivity was affected.
Semi-acute pelvic infection
- In this case, the symptoms appear gradually.
- Lower back pain.
- I was feeling sick.
- Mild abdominal pain.
- Irregular change in body temperature.
- Vomit.
Subacute pelvic infections can be hard to diagnose since the symptoms appear slowly and, like other pregnancy disorders, are acute or subacute. The consequences of infection of this organ cannot be ignored.
Kidney ulcer:
This can lead to high blood pressure and kidney failure in the future.
Complications of kidney infection during pregnancy include:
Purifies all excess blood and reuses the purified blood within the body. Infection of this part of the body causes bacteria to enter the bloodstream and cause blood poisoning.
Complications of kidney infection in pregnancy include:
An infection of this part of the body causes an increase in bacteria in the bladder and fluid. This can result in the sac rupturing and premature birth. Low birth weight babies are born as a result of premature birth. A pelvic infection with high fever is a serious type of infection of this organ that can lead to miscarriage. If you suffer from severe back or side pain, vomiting, and fever, these could indicate an infection of this organ.

Pregnancy and kidney stones
are caused by the accumulation of chemicals in the urine. Rocks are formed when the concentration of these substances reaches a certain level. Is it true that urinary tract stones, especially kidney stones, can cause abdominal pain during pregnancy? The occurrence of kidney stones in pregnancy is rare, but its correct and timely diagnosis can reduce pain and prevent preterm delivery. Most stones are small and pass through the urethra, but larger stones require medical intervention and treatment.
Pregnant women are slightly more likely to develop kidney stones than non-pregnant women, according to new research. In a study of 3,000 pregnant women at the Mayo Clinic, researchers found that pregnancy increases the risk of kidney stones, which increases in the third trimester and near delivery, and decreases one year after delivery.
Is the appearance of kidney stones dangerous during pregnancy? There is no doubt that kidney stones pose more health risks and complications for pregnant women and should be taken into account. In addition to causing changes in body water and electrolyte levels, it is also very painful. Preeclampsia (hypertension), urinary tract infections, or premature birth are usually the results of this complication.
During pregnancy, doctors recommend controlling body weight, drinking plenty of fluids, following a low-salt diet, and getting at least 1000 mg of calcium a day from food instead of calcium supplements.
Pregnancy kidney stones can cause several complications.
The risk of kidney stones during the first months of pregnancy is very low, and most kidney stones occur during the second and third trimesters. If the mother has small, crystalline stones before pregnancy, and as the pregnancy progresses and the body changes, the stones will grow.
Crystal stones do not have any obvious symptoms and can only be detected using ultrasound. Therefore, if you have a history of kidney stones, we recommend having a kidney examination and ultrasound by a urologist before you become pregnant.
The symptoms of kidney stones in pregnancy are often caused by obstruction of the blood vessels or urinary tract. These symptoms include:
Pain while urinating: This pain is often so severe that it can make urination unbearable. Due to the frequent urination, this condition is very annoying.
You may experience nausea or vomiting due to excessive pain from kidney stones or accumulation of urine in the kidneys.
Hematuria or the presence of blood in the urine is very worrying for pregnant women. Pregnant women are afraid it will be an indication of an abortion. A bloody urine caused by kidney stones is not a serious health concern in itself.
An ache in the back, sides, abdomen, and groin: This may indicate urinary retention in one or both kidneys caused by obstruction of the kidney stones. In later stages of pregnancy, stretching and swelling in the kidneys may also occur due to an accumulation of urine, a condition known as hydronephrosis. In the last months of pregnancy, the fetus begins to produce urine. This is why kidney stones can complicate the treatment of hydronephrosis in pregnancy.
Causes of kidney stones during pregnancy
Pregnant women experience physiological changes that increase their risk of developing kidney stones, especially in the third trimester. These changes include:
During pregnancy, certain physiological changes can affect a woman’s urinary tract, causing an increase in the size of her previous urinary stones or even the possibility of a new kidney stone forming.
The size and position of the uterus can limit urine output in late pregnancy. The ureters (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder) usually dilate during pregnancy, making urination difficult. Hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidneys) can result from this. The size of the ureters increases by approximately 1 cm due to the increase in vascular volume and interstitial space within the kidney. Additionally, the collecting system and ureters lose their ability to contract, causing dilation and sometimes pain. Infection or stones can develop if the urine is not completely excreted.
Various changes in the amount of vitamins and minerals can also lead to kidney stones during pregnancy. In this case, the body tends to excrete calcium less and transfer it more to the fetus.
Infections of the urinary tract, which are common during pregnancy, may also contribute to kidney stones.
The body requires more water during pregnancy.
Can kidney stones harm a pregnant woman?
The following risks may occur if kidney stones are not excreted during pregnancy:
Induction of preterm labor
causes excruciating pain
due to preeclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy)
infection of the urinary tract, or even sepsis
Natural childbirth may progress abnormally
Even though these risks do not directly cause miscarriage, they do increase the risk. Consequently, both patients and physicians should be aware of these risks. Kidney stones are particularly dangerous during pregnancy.
How to prevent kidney stones during pregnancy
is definitely the best way to avoid urinary stones during pregnancy. Here are a few tips:
Keep your body hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, including water.
Don’t hold your urine and empty it as soon as possible.
Cut down on foods high in oxalate, such as nuts, chocolate, dark green leafy vegetables, and berries.
If you have a history of kidney stones, tell your obstetrician before planning a pregnancy.
Always exercise and exercise as directed by your doctor.
You should see a gynecologist if you experience severe abdominal pain.
How to diagnose kidney stones during pregnancy
Diagnosing and treating kidney stones during pregnancy can be challenging. By the end of the first trimester, 80 to 90% of urinary stones are diagnosed. There are currently several ways to diagnose this disease, which we will discuss below:
A urine analysis and culture can help diagnose urinary tract infections caused by kidney stones. It is also necessary to check blood creatinine and uric acid levels. Elevated serum calcium levels usually require further evaluation.
Although ultrasound is the first option for diagnosing kidney stones in pregnant women, it doesn’t always reveal them. Other imaging techniques are needed in acute cases.
Magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance urography are usually used for radiological diagnosis. Radiation risks depend on the age of the fetus. Pregnancy is contraindicated because X-rays can cause abnormalities in the fetus. Ideally, ionizing radiation should not be used during the first or second trimester.
Intravenous urography or CT scan: These options are only used in pregnant women if symptoms persist or if other complex problems arise.
During a nuclear radiograph, a radioisotope is injected into a pregnant woman’s vein, allowing a radiologist to examine the kidneys more closely.
Diagnosing kidney stones during pregnancy
and treating them in pregnancy to prevent premature birth
What is the best way to treat kidney stones during pregnancy? It is difficult to treat kidney stones during pregnancy as it can have both side effects on the mother and harm to the fetus. Pregnancy conditions can eliminate many of the treatment options regardless of the size of the stone. Here are the most common ways to treat kidney stones during pregnancy:
How to treat kidney stones during pregnancy
Conservative treatments for kidney stones during pregnancy
When pregnant women have kidney stones, they are first advised to rest, drink plenty of fluids, and use medications such as stone crushers and muscle relaxants to relieve the ureter. Most stones (70-80%) go away on their own with conservative treatment.
Invasive treatments are not recommended in pregnancy.
The doctor may have to intervene severely if there are stones 5 mm or larger if there is any manipulation of the bladder, pelvis, ureter, or kidney.
Stenting: In this procedure, a stent or PCN tube is inserted into the ureter. By doing this, the urine can easily be excreted with the stone and the burden on the urinary tract is reduced. A tube is usually not removed until the end of pregnancy.
The extrinsic wave crushing (ESWL) method uses a device to irradiate ultrasonic pulses to the body and break kidney stones. Using this method during pregnancy is absolutely harmful to the fetus and can even result in its death. However, it is highly recommended for women who are not pregnant.
As an alternative to ESWL, urethroscopy is recommended for pregnant women in acute and complex conditions. A narrow, flexible tube called a scope is inserted into the urethra through the genitals while, at the same time, other devices are used to crush the kidney stone. As the surgeon looks inside the monitor, a camera is at the end of the scope tube.
Laparoscopic equipment is used for percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL). While it is safe and effective for non-pregnant women, it is not recommended during pregnancy.
Why do children and infants get kidney stones?
Kidney stones are more likely to develop in children who are in a condition that increases their risk. However, some people get kidney stones without apparent cause. A relative with kidney stones can increase a person’s risk of developing kidney stones as well. Children and adolescents who have already had kidney stones are more likely to get them again.
Additional risk factors include:
Not drinking enough fluids can cause urine to thicken as a result of dehydration. This increases the possibility of crystal formation.
Drinking a lot of sweets, caffeinated substances or sports drinks, as well as eating a high salt diet can increase the risk of calcium stones. Being overweight can also increase the risk of kidney stones in children.
A structural defect in the urinary tract can block the flow of urine and allow urine to collect like a small pool. The crystalline components of urine can coalesce to form stones when the flow of urine ceases.
If taken in high doses, some medications can increase the risk of kidney stones.
Disorders of the metabolism (difficulty breaking down or consuming food) can lead to oxidation of oxalate (a substance produced in the body by certain foods) or cystine in the urine.
The genetic disease cystinuria causes excessive excretion of cysteine from the kidneys and the formation of cystine stones.
Some diseases and conditions can increase the risk of kidney stones, including gout (a type of arthritis), other kidney diseases, conditions affecting the thyroid or parathyroid glands, and some system infections.

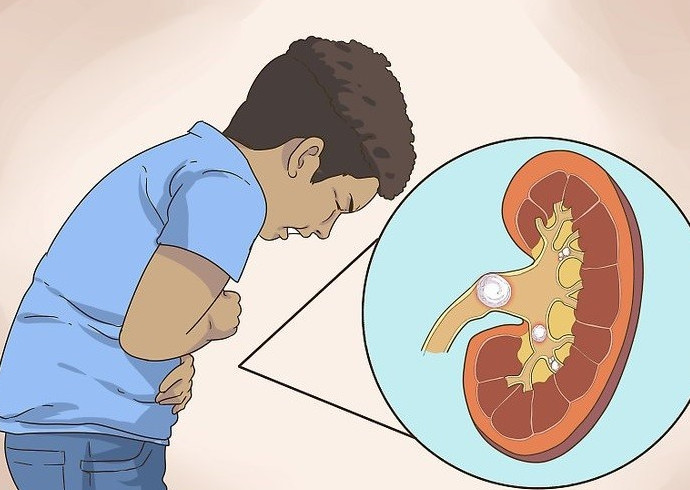
What are the symptoms of kidney stones in children?
Most kidney stones do not cause symptoms until they move around the kidneys or pass through the ureter. Small stones can pass through the urethra without pain or complications.
However, large stones can block the urinary tract and cause symptoms such as:
Back and side pain
The movement of urine in the urethra causes pain in the lower abdomen.
Waves of pain come and go.
Blood in the urine (may be red or brown) is called hematuria.
Requires frequent or urgent urination
Fever or chills
A large stone can form a mass that causes one or both kidneys to swell (this is called hydronephrosis). This can cause back and side pain. If left untreated, it can cause long-term kidney damage. However, many kidney stones do not cause permanent damage.
How are kidney stones diagnosed?
Consult your doctor as soon as possible if your child exhibits any of the following symptoms:
Side pain
Blood in the urine
Other kidney stone symptoms
If your child shows any of the following symptoms, visit your clinic or emergency hospital immediately:
Nausea, vomiting, fever, chills
and difficulty urinating
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and how long they have been present. The baby’s diet; Things that may cause dehydration; and any history of kidney stones in the family. Examines any operation or disease affecting the kidneys or urinary system.
In addition to a physical exam, your doctor may order a blood test, urine test, or kidney function test to check for kidney stones. Imaging tests (such as ultrasound, X-rays, or CT scans) are often used to examine the kidneys more thoroughly. The size and location of a stone can be determined by imaging tests, which help doctors decide the best treatment.

Treatment in a hospital
When a kidney stone blocks the urethra or causes severe pain or dehydration, you may need to go to the hospital. In the hospital, the child may receive intravenous fluids and painkillers to treat or prevent kidney stones and dehydration.
Large rocks are rarely moved on their own. If you have large stones or stones that damage your kidneys, you should seek medical attention:
shock wave crusher removal. By using sound waves or shock waves, kidney stones are broken up into smaller pieces that can be excreted in the urine.
Urotroscopy is the procedure used to remove kidney stones. It involves a small tube with a camera at the end. A tube is inserted into the bladder through the urethra after the patient is anesthetized. The tube is then inserted into the ureter and kidneys to find the stone. Urotroscopes have special tools that can separate stones from the urethra or cut them into smaller pieces.
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy is used to remove large stones or stones located near the kidney. A small incision is made in the kidney to insert an endoscope to remove the stone. An ultrasonic probe can shatter large rocks into smaller pieces through shock waves, making them easier to pass through urine. The majority of people who undergo kidney surgery stay in the hospital for a few days.
To remove large stones, open surgery called nephrolithotomy is performed in rare cases. The procedure involves making an incision in the side to reach the kidney. X-ray imaging is used during surgery to detect kidney stones. They are then removed from the kidney and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Follow-up care is necessary after treatment.
Children with kidney stones are examined by doctors to prevent recurrences. You may be asked by your pediatrician to have a 24-hour urine collection test. The purpose of this is to measure the volume of urine over 24 hours and to examine the content.
As a result of your child’s kidney stones, your doctor may prescribe treatment or medications to reduce the amount of substances that cause crystals to form in your urine.

Treatment of kidney stones with herbs
Herbal treatments are available for treating kidney stones, a common disease.
Drink lemon juice and Delster to get rid of kidney stones
When a person has kidney failure, they should know that drinking water for eight glasses and a lot of water when they are healthy is enough.
drinking a lot of water has little effect on the movement of kidney stones, but it can never break the central nucleus of the stone and expel the stone.
Drinking lemon juice and bitter delster is very effective in getting rid of kidney stones since lemon juice breaks down kidney stones and bitter delster causes the excretion of broken body, stones, and sand from the kidneys.
Melon eliminates kidney stones :
Eating melon can eliminate kidney stones. Blend the melon and its seeds in a blender, and use as a mixture of two meals per day.
Consume almond oil to prevent kidney stones :
Almond oil has a great effect on the elimination of kidney stones. The consumption of a teaspoon of almond oil for ten days can help people get rid of stones.
Kidney stones can be excreted with strawberry leaves :
Strawberries can be used to treat kidney stones. Boil 40 grams of strawberry leaves in a liter of water for 3 to 4 minutes. Drink this solution every five hours.
Remove kidney stones by drinking celery juice :
Before each meal, drink half a glass of celery juice with spring orange juice to prevent kidney stones.
Remove kidney stones with persimmon seeds :
You can also use roasted persimmon seeds, such as ground persimmon seeds, to treat kidney stones. Simply brew a teaspoon of the powder in a glass of boiling water for 20 minutes. Drink this drink for 3 days to help eliminate stones.
How to remove kidney stones with cheese :
For people with kidney stones, boil 100 grams of cheese leaves in one and a half liters of water for 2 to 3 minutes, strain it, and pour it into a glass with a tablespoon of olive oil.

The relationship between salt intake and kidney stones:
People need to keep their bodies hydrated and hydrated in order to get rid of excess salt. Drink at least six to eight glasses of water each day.
Today, salt is an important factor for health. Furthermore, none of us can imagine cooking without salt because we believe that food without salt will not taste good, and long-term use of salt will severely impact our health. This is especially true for kidney health. Excess salt should therefore be avoided in our diet.
Kidneys are the body part that is most affected by high salt intake. In addition to purifying and purifying 5 liters of blood each day, the kidneys also excrete toxins and excess substances from the body that, if left in the body, can cause illness or death. In this part of Namnak, we will investigate the effects of high salt consumption on kidney health.
Try replacing salt in your kitchen with a healthier option that still tastes good, such as:
powdered onion
powder or garlic powder
Soy sauce with low sodium
Lemon juice
Pepper
Ginger
Turmeric
Cumin
Oregano

In many foods, turmeric alone can serve as a substitute for salt. Alternatives mentioned above can be used for a variety of foods and we are confident you will enjoy the new flavors.
Using this list, you can change your diet and see the results.
You can also completely eliminate salt from your diet depending on the season. While sodium is also essential for good health, remember that there are many foods you can consume during the day that have enough sodium.
The kidneys filter between three and five grams of sodium-rich foods per day.
The pH is changed by salt :
When you consume more than 5 grams of salt during the day, it is stored in the blood and generally causes your body to become acidic, while the alkaline level in your body should always be higher. Acidification of the body has the following consequences:
Kidney disease and heart disease.
Chronic fatigue
Difficulty concentrating
Fragile nails
joint’s pain
Susceptible to infection
Joint pain
Salt interferes with the clearance of blood :
A high-salt diet begins to show its effects around the age of 40. People suffer from high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high fat, metabolic changes, etc. Some also suffer from kidney problems caused by high salt intake and low water intake.
As the body is made up of 60% water, when there is a lot of salt in the body, the organs and tissues become full of salt, so the kidneys cannot completely remove the salt from the body. When you have water retention in your body, toxins can also irritate your tissues, resulting in symptoms of kidney problems and toxins in your bloodstream, such as swelling of the legs, chronic fatigue, bloating, or abdominal pain.
Salt causes aging and kidney damage :
The more salt you consume, the harder your kidneys have to work to detoxify your body, so consuming less water with it exacerbates this condition and accelerates the aging of the kidneys. This can be detrimental to your overall health.
Some of the direct and indirect effects of high salt intake include :
cardiovascular disease
arthritis and rheumatism
loss of hair
problems with the skin
Digestive problems
also read :
The kidney and their diseases – everything we need to know


