What is vegetarian food? A vegetarian diet includes a diverse combination of plant foods, which include: fruits, vegetables, grains, healthy fats and proteins, in addition to these foods, it is usually recommended to use a variety of protein-rich plant foods to replace protein. These foods include: nuts, seeds, legumes.

Foods that are recommended include:
Leafy greens, asparagus, and broccoli are dark green vegetables.
Tomatoes and carrots are red and orange vegetables.
Vegetables and starches
Beans, lentils, peas, and chickpeas are legumes.
Grains such as quinoa, barley, buckwheat, rice, and barley are whole and refined grains.
Foods rich in protein include eggs, dairy products, legumes, and soy products
A variety of nuts, such as almonds, walnuts, and cashews
Coconut oil, olive oil, and avocados are healthy fats.
Apples, bananas, berries, oranges, melons, pears, and peaches are examples of fruits.
As some nutrients in plant sources are less available or more difficult to absorb than those in meat or fish, it is very important to diversify the food sources consumed, and contrary to popular belief, vegetarians usually consume enough protein. The vegetarian diet provides iron and calcium from dairy products, but if the diet is not properly planned, the body may lack essential nutrients, such as iron and vitamin B12.
Vegetarians’ nutritional requirements are shown below, along with their sources:
| Nutritional element | Required for adults 19 and older | food sources |
|---|---|---|
| iron | 8 to 18 mg | Consuming whole grains, including beans, chickpeas, tofu, lentils, spinach, cashews, and green peas along with vitamin C is recommended to help the body absorb iron. |
| Calcium | 1000 to 1200 mg | Yogurt, milk, cheese, tofu, fortified orange juice, kale leaves, broccoli and kale. |
| Protein | 46 to 56 grams | Eggs, milk, soy milk, nuts, nut butters, seeds, grains, and plant sources may not contain complete protein, so people should make sure they get enough of all types of protein throughout the day. |
| Vitamin D | 15 to 20 micrograms | Fortified dairy products, soy milk, and breakfast cereals, plus sun exposure. |
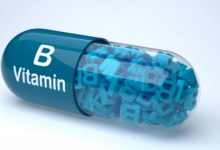
| Vitamin B12 | 2.4 micrograms | Yeast, eggs, dairy products and fortified foods such as breakfast cereals. |
| Zinc | 8 to 11 mg | Dairy products, fortified cereals, dried beans, nuts and soy products. |
| Iodine | 150 micrograms | Seaweed, yogurt, milk, cheese, enriched bread, enriched pasta, prunes, apple juice, green peas and bananas. |
| Omega 3 | 1.6 grams for males and 1.1 grams for females | Linseed oil, canola oil, soybean oil, tofu, walnuts and eggs enriched with omega-3. |
How does a vegetarian diet work?
Vegetarian diets are defined as diets based on plant-based foods, and most doctors and nutritionists agree that a low-fat diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and nuts is beneficial to human health. Vegetarian diets provide a variety of healthy and nutritious foods, but what an individual eats depends on their personal food choices and the type of vegetarian diet they follow.
Can a vegetarian diet help you lose weight?
Despite the fact that vegetarian diets are not considered weight loss systems, people who follow them tend to weigh less than others, possibly because they consume more vegetables. Vegetarian foods that increase feelings of satiety and are low in calories and fat may contribute to weight gain if portion sizes are large. To maintain or lose weight, the most important rule is to follow a healthy diet with limited calories, which includes: sweets, sweet drinks, in addition to foods.