Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are used to replace missing or damaged teeth. They have been in use for many years and have become increasingly popular due to their natural appearance and functionality. The concept of dental implants dates back to ancient times, where the use of shells, stones, and other materials were used to replace missing teeth.
Dental implants: Aftercare advice :
Dental implants have revolutionized the field of dentistry and have provided a long-term solution for patients with missing teeth. They are made from biocompatible materials such as titanium, which are capable of fusing with the jawbone and providing a stable foundation for a replacement tooth. Dental implants can be used to replace a single tooth, multiple teeth, or even a full arch of teeth.
The need for dental implants arises from a variety of reasons, including tooth decay, injury, gum disease, or congenital defects. Dental implants can provide a durable and long-lasting solution for patients who are experiencing dental issues, allowing them to eat, speak, and smile with confidence.
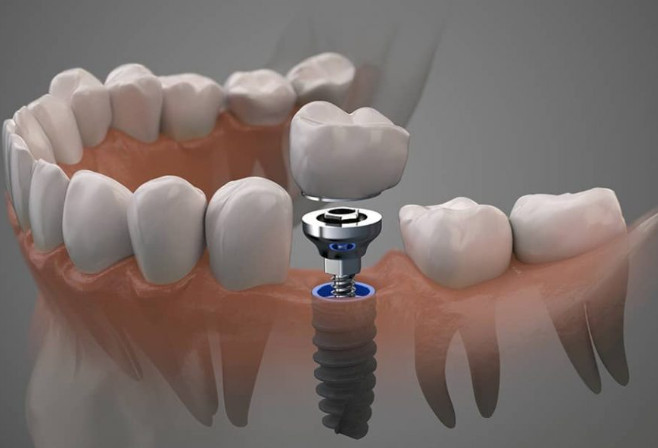
In this article, we will discuss important facts about dental implants and how to care for them properly. We will also address common misconceptions about dental implants and highlight the advantages and disadvantages of this treatment option. Finally, we will explore future advancements in dental implant technology and their potential impact on the field of dentistry.
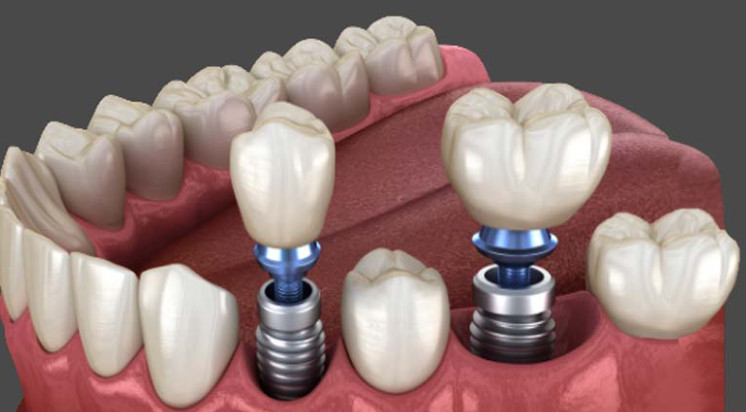
2. Types of Dental Implants
There are several types of dental implants, each designed to address specific dental needs. The most commonly used types of dental implants are endosteal implants, subperiosteal implants, zygomatic implants, and All-on-4 implants.
Endosteal implants are the most popular type of dental implant and are used to replace individual teeth or multiple teeth. They are placed directly into the jawbone and provide a stable foundation for a replacement tooth. Endosteal implants are made of titanium and are shaped like screws or cylinders.
Subperiosteal implants are used when there is not enough bone density to support an endosteal implant. They are placed on top of the jawbone and under the gum tissue. Subperiosteal implants are typically used to replace multiple teeth and are made of a metal framework.
Zygomatic implants are used when there is not enough bone density in the upper jaw to support an endosteal implant. They are anchored in the cheekbone, providing an alternative to bone grafting. Zygomatic implants are typically used for patients who have severe bone loss in the upper jaw.
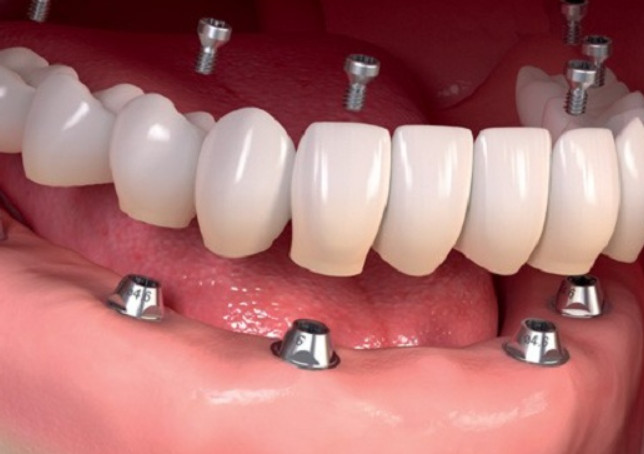
All-on-4 implants are a type of dental implant that is used to replace a full arch of teeth. They use four implants strategically placed in the jawbone to support a full set of replacement teeth. All-on-4 implants are typically used for patients who have lost most or all of their teeth and want a long-term solution.
The type of dental implant used will depend on several factors, including the number of missing teeth, the location of the missing teeth, and the amount of bone density present in the jawbone. Your dentist or oral surgeon will evaluate your individual needs and recommend the best type of dental implant for you.
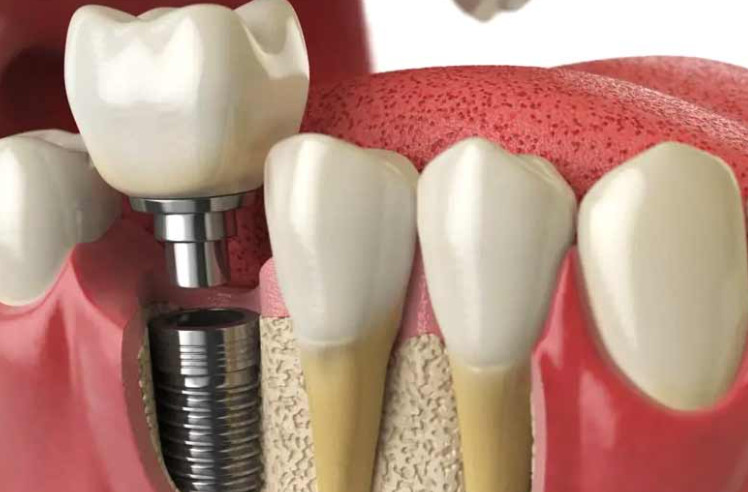
3. The Dental Implant Procedure
The dental implant procedure typically involves several steps, including consultation and evaluation, preparing for surgery, implant placement, healing and osseointegration, and attaching the abutment and crown.
Consultation and evaluation: Before the dental implant procedure, you will meet with your dentist or oral surgeon for a consultation and evaluation. This will involve a thorough examination of your teeth and gums, as well as a review of your medical history. Your dentist or oral surgeon will also take x-rays and impressions of your teeth to help determine the best course of treatment.
Preparing for surgery: Once your dentist or oral surgeon has determined that you are a good candidate for dental implants, you will prepare for the surgery. This may involve taking antibiotics or other medications to prevent infection, as well as avoiding certain foods and drinks before the surgery.
Implant placement: The first step of the surgery involves placing the implant directly into the jawbone. This is done under local anesthesia, and the implant is typically placed using a surgical guide to ensure accuracy. Once the implant is in place, the gum tissue is sutured closed, and a temporary crown may be placed on top of the implant.
Healing and osseointegration: After the implant is placed, a process called osseointegration begins. This is the process by which the implant fuses with the jawbone and becomes a stable foundation for the replacement tooth. This process can take several months, and you will need to maintain good oral hygiene during this time to ensure proper healing.
Attaching the abutment and crown: Once osseointegration is complete, your dentist or oral surgeon will attach the abutment to the implant. The abutment is a small post that connects the implant to the replacement tooth. Finally, a custom-made crown is attached to the abutment, providing a natural-looking and functional replacement tooth.
The dental implant procedure is typically performed in stages, with several weeks or months between each stage to allow for healing and osseointegration. The length of the procedure will depend on the number of implants being placed and the individual needs of the patient. Your dentist or oral surgeon will provide you with detailed instructions on how to care for your dental implants following the procedure.
4. Care and Maintenance of Dental Implants
Proper care and maintenance of dental implants are essential to ensure their longevity and success. Good oral hygiene is key to keeping your dental implants healthy and functional. Here are some tips for caring for your dental implants:
1. Brush and floss regularly: Just like natural teeth, dental implants require regular brushing and flossing to prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria. Brush at least twice a day and floss at least once a day.
2. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush: To avoid damaging the implant or surrounding gum tissue, use a soft-bristled toothbrush. You can also use an interdental brush to clean around the implant and remove any debris.
3. Use non-abrasive toothpaste: Avoid using abrasive toothpaste, which can scratch the surface of the implant and make it more susceptible to bacteria buildup. Instead, use a non-abrasive toothpaste recommended by your dentist.
4. Avoid hard or sticky foods: Hard or sticky foods can damage the implant or the crown attached to it. Stick to softer foods, and cut harder foods into small pieces to make them easier to chew.
5. Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups are important for maintaining the health of your dental implants. Your dentist will monitor the condition of your implants and perform any necessary adjustments or repairs.
6. Quit smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of implant failure by inhibiting the healing process and reducing blood flow to the gums. If you smoke, quitting is essential to the success of your dental implants.
7. Consider a mouthguard: If you grind your teeth at night, a mouthguard can help protect your dental implants from damage.
Following these tips can help ensure the long-term success of your dental implants. If you experience any pain, discomfort, or other issues with your implants, be sure to contact your dentist or oral surgeon as soon as possible.
