What is liver cirrhosis? How is it treated?
Cirrhosis is a stage of liver ulcer (fibrosis) in many types of liver disease, such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism. Whenever your liver is damaged due to illness, alcohol consumption, or any other reason, the liver tries to heal; in the process, a wound is created on the wound. Advanced cirrhosis is life-threatening, and liver cirrhosis cannot be prevented in general. However, if liver cirrhosis is diagnosed and treated early, the damage can be limited.
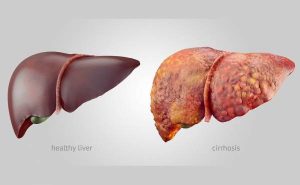
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis:
Cirrhosis often has no signs or symptoms unless the liver is severely damaged. Signs and symptoms of this disease may include the following:
- Fatigue
- Bleeding or bruising that is easily seen
- Anorexia
- nausea
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Weight Loss
- skin itching
- Yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen
- Blood vessels like spiders on the skin
- Redness of the palms
- For women, deficiency or delay in menopause
- For men, loss of sexual power, breast enlargement, or shrinkage of the prostate
- Dizziness, snoring, and stuttering (hepatic encephalopathy)
When to see a doctor?
If you have any of the signs and symptoms listed above, make an appointment with your doctor.
Causes of liver cirrhosis:
A wide range of diseases and conditions can damage the liver and lead to cirrhosis.
Some of the reasons are:
- Chronic alcoholism
- Chronic viral hepatitis (hepatitis B, C, and D)
- Fat accumulated in the liver (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease)
- Accumulation of iron in the body (hemochromatosis)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Copper in the liver (Wilson’s disease)
- Bile duct weakness (biliary atresia)
- Lack of alpha antibodies 1
- Impaired sugar metabolism (galactosemia or glycogen storage disease)
- Genetic disorder (Alagil syndrome)
- Liver disease due to weakened immune system (immune hepatitis)
- Bile duct destruction (primary cirrhosis)
- Healing and use of bile ducts (primary sclerosis)
- Infections such as syphilis or brucellosis
- Medications, including methotrexate
Risk factors and worsening of liver cirrhosis:

Drinking too much alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption is a risk factor for cirrhosis.
Viral hepatitis
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis has cirrhosis of the liver, but it is a significant cause of liver disease.
being overweight
Obesity increases the risk of cirrhosis, such as non-alcoholic trans fats and hepatitis status.
Problems and complications of liver cirrhosis:
High blood pressure in the arteries that supply the liver
Cirrhosis reduces the normal blood flow through the liver, thereby increasing the pressure on the blood vessels that receive blood from the intestines and spleen.
Spleen enlargement (splenomegaly)
Portal hypertension can cause swelling and entrapment of the spleen, trapping white blood cells and platelets. White blood cells and platelets in your blood can be the first sign of cirrhosis.
Swelling in the legs and abdomen
Increased pressure in the portal vein can cause fluid in the legs (swelling) and abdomen (fluid stones). Swelling and ascites may also be due to the liver’s inability to produce specific blood proteins such as albumin adequately.
Bleeding
Portal hypertension can cause blood to flow to smaller arteries. With extra pressure, smaller vessels can cause severe bleeding. Blood pressure can cause blood vessels (varicose veins) to expand in the esophagus or stomach (varicose veins) and lead to fatal bleeding.
Infection
If you have cirrhosis, your body will have a complex time-fighting infection. Ascites can lead to bacterial infections, severe conditions.
Malnutrition
Cirrhosis nutrients are tough to process in the body, which can lead to weakness and weight loss.
Toxic production in the brain (hepatic encephalopathy)
The liver damaged by cirrhosis is unable to excrete toxins from the blood and have a healthy liver. These toxins can accumulate in the brain, causing mental confusion and difficulty concentrating, and over time, hepatic encephalopathy can go unanswered.
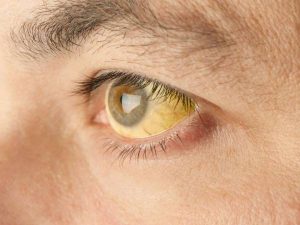
Jaundice
Jaundice occurs when a patient’s liver does not clear enough bilirubin from your blood. Jaundice causes yellowing of the skin, whitening of the eyes, and darkening of the urine.
Bone disease
Some people with cirrhosis lose their bones and are more prone to fractures.
Increased risk of liver cancer
Many people with liver cancer have had previous cirrhosis.
Acute and chronic cirrhosis
Researchers now believe that this is a definite problem in some people with cirrhosis but do not fully understand the causes.
Prevention of liver cirrhosis:
Reduce your risk of cirrhosis by taking the following steps to take care of your liver:
If you have cirrhosis, do not drink alcohol, and you should avoid alcohol if you have liver disease.
healthy diet
Choose a vegetarian diet rich in fruits and vegetables. Choose whole grains and lean protein sources and reduce the amount of fatty and fried foods.
Have a healthy weight
Excess body fat can damage your liver. If you are obese or overweight, talk to your doctor about a weight loss program.
Reduce the risk of hepatitis
Sharing syringes and having unprotected sex can increase the risk of hepatitis B and C, and ask your doctor about hepatitis vaccination. If you are concerned about the risk of liver cirrhosis, talk to your doctor about ways to reduce the risk.
Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
People with primary liver cirrhosis have no symptoms. Often, cirrhosis is first diagnosed through a routine blood test or examination. A combination of laboratory tests is usually done to help confirm the diagnosis.
the experiment
Your doctor may order one or more tests that may diagnose your liver problem, including:
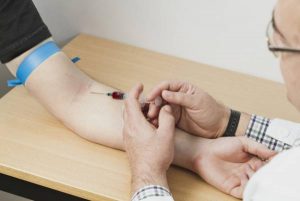
Laboratory tests
Your doctor may test your blood for signs of liver dysfunction, such as excess bilirubin, as well as certain enzymes that may indicate liver damage. Based on your blood test results, your doctor may be able to diagnose the underlying cause of the cirrhosis and may also use a blood test to determine if the cirrhosis is severe.
Imaging tests
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) can be recommended. This advanced imaging test detects hardening of the liver. Other imaging tests, such as MRI, CT, and ultrasound, may be done.
Sampling
It is not necessary to detect tissue samples. However, your doctor may use it to diagnose the severity, extent, and cause of liver damage.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis:
Treatment for cirrhosis depends on the cause and extent of the damage to your liver. May need to be hospitalized.
Treatment of the leading cause of cirrhosis:
In primary cirrhosis, treatment of the underlying cause may be initiated to minimize liver damage.
These options include the following:
Treatment of alcoholism
People with cirrhosis should drink alcohol due to overdose. Stop drinking because any amount of alcohol is vital to the liver.
Weight loss will be followed by fatigue and constant tiredness.
Medications to control hepatitis
Medications may cause more damage to the liver cells caused by hepatitis B or C.
Medications to control other causes and symptoms of cirrhosis
Medications may slow the progression of certain types of liver cirrhosis. Other drugs may relieve specific symptoms such as itching, fatigue, and pain.

Treatment of complications of liver cirrhosis:
Excess body fluids
A low-sodium diet and medication to prevent fluid retention in the body may help control swelling.
Portal blood pressure
Some blood pressure medications can control high blood pressure in the liver’s blood vessels and prevent heavy bleeding. If you have varicose veins, you may need a prescription to reduce the risk of bleeding. If you have symptoms of bleeding, you may need a procedure (bandage closure) to prevent bleeding or reduce the risk of further bleeding.
Infection
You may be taking antibiotics or other treatments for the infection. Your doctor may also recommend vaccinations against the flu, pneumonia, and hepatitis.
Increased risk of liver cancer: Your doctor may perform tests to determine if you have liver cancer
Hepatic encephalopathy
You can use drugs that reduce the accumulation of toxins in the blood due to poor liver function.
Liver Transplant
In advanced cirrhosis cases, a liver transplant may be the only treatment option when the liver fails. Liver transplantation is replacing a diseased liver with a healthy liver from a deceased donor or part of a liver from a living donor.
There are 8 home remedies for liver cirrhosis:
Quit alcohol
Alcohol damages liver cells, so it makes your condition worse.

Milk thistle
Preliminary research suggests that this plant may be beneficial for people with alcohol-related liver disease, but more research is needed. Milk thistle is available in liquid, capsule, and tincture form.
Note: Milk thistle may not be suitable for people suffering from varicose veins or inflammation caused by cirrhosis.
Also, it is not recommended for people with a history of hormone-related illnesses.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture helps relieve discomfort such as fatigue caused by liver cirrhosis. Do your acupuncture with a specialist.
There are many acupuncture points for treating cirrhosis, but they are used depending on the specific clinical signs and symptoms.
Papaya seeds
Try some fresh papaya seeds and consume one tablespoon of its extract. Add ten drops of lemon juice. Drink once or twice a day for one month.
Antioxidants
Eat fruits, vegetables, and whole grains such as berries, spinach, carrots, artichokes, garlic, Brazil nuts, etc., as part of your daily diet.
Vegetables such as broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts also help detoxify the liver. Also, drink 1-2 glasses of raw vegetable juice daily.
Schisandra
This plant is used in traditional Chinese medicine to purify the liver, protect liver cells from further damage and help regenerate liver tissue.
You can choose Schisandra and Stragal as supplements. Consult your doctor for proper and helpful use.
Green tea
Add a teaspoon of green tea powder (or a green tea bag) to a cup of warm water. Let stand 5 minutes. Strain (if using a green tea bag, remove the bag), then sweeten it with a bit of honey. Drink this tea three times a day.

Vitamin C
Drink two tablespoons of fresh orange juice three times a day for 15 to 20 days. Add other foods rich in vitamin C, such as raspberries and lemons.
Other recommendations for liver cirrhosis:
- Have a balanced and proper diet.
- Limit your protein and salt intake. Preferably choose plant protein instead of animal protein.
- Avoid processed foods and junk foods because they are not suitable for liver health.
- Constipation causes toxins to build up that may return to the liver.
- Exercise regularly because, in addition to fitness, it neutralizes fatigue and strengthens muscles.
- Take 1200 mg of S-Adenosylmethionine (SAMe) daily to improve liver function.
- Licorice is also helpful in preventing liver damage and also helps treat hepatitis C infections.
- You can drink it as an herbal tea or as a supplement to improve liver function.
- But before using this plant, consult your doctor because it is not suitable for people with high blood pressure and may interfere with certain medications.
- Cirrhosis can make your liver sensitive to certain medications.
- So talk to your doctor before taking medicine.