What are the types of Low back pain? List of types and treatment
Low back pain is one of the most common reasons for patients to go to hospitals. Patients often have the following three mistakes about back pain:
- It is thought that any back pain is due to a disc protrusion.
- MRI is thought to be necessary for any low back pain.
- Some seek only pain relief and do not examine chronic low back pain.
Anatomy and structure of the vertebrae and lumbar spine
Our waist is made up of several beads.
An intervertebral disc separates the beads.
The spinal cord is located inside the posterior ring of the vertebrae.
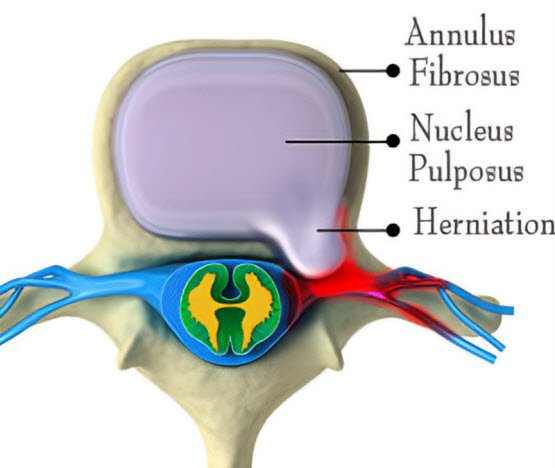
The intervertebral disc consists of a peripheral fibrous ring (annulus fibrosus) and a central gelatinous nucleus (nucleus pulposus). (Everything About Knee Pain From Causes To Treatment And Prevention)
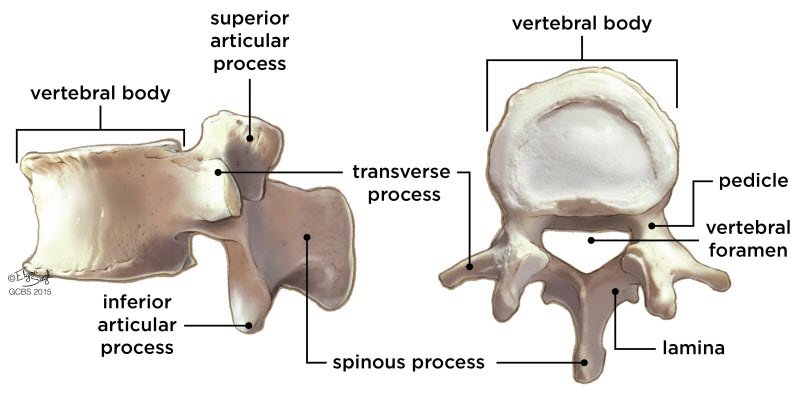
With age, the fibrous part gradually dries out, and the height of the disc between the vertebrae decreases. These changes manifest as pain and dryness, and sometimes as a disc herniation between the vertebrae.
The disc herniation between the lower back’s vertebrae causes pressure on the nerve roots inside the spinal canal.
Pressure on the spinal cord causes paralysis and increased reflexes. If a hernia occurs in the lower back, where the spinal cord is exhausted, and only the nerve root is present, the paralysis will cause the reflex to disappear.
Types of Low back pain
Back pain can be due to a problem with the back itself and problems with nearby structures and organs. The second type of pain is called back pain. In this type of low back pain, changing the position does not affect it.
For example, inflammation of the pancreas, pancreatitis, dilatation of the aortic artery, or kidney infection may manifest as low back pain.
If the pain is of vertebral origin, it may present as localized back pain or pain referred to the buttocks or lower limbs. The upper lumbar vertebral disease causes pain that refers to the lower back, groin, or front of the thigh, and lower lumbar vertebral disease causes pain in the buttocks, back of the thigh, back of the leg, or leg.
Radicular pain is a sharp pain that shoots down from the lower back to the lower extremities and is triggered by coughing, sneezing, or a voluntary contraction of the abdominal muscles (when lifting heavy objects or defecating). Maneuvers that involve the nerve or nerve roots involved cause pain.
But be aware that many spinal diseases may be due to spasms of the muscles around the waist.
How to check for Low back pain?
Back pain lasting less than three months is called acute.
The patient should first be evaluated for severe illnesses such as infection, cancer, and trauma.
Risk factors for serious illness, infection, tumor, or fracture in patients with acute back pain include:
Exacerbation of pain at rest or night
Personal history of cancer with a history of chronic infection, especially in the lungs, skin, or urinary tract
History of trauma
Incontinence
Age over 70 years
Injecting drug addiction
Corticosteroids
Unexplained fever and unexplained weight loss
Pain when hitting the spine
Abdominal, rectal, or pelvic mass
Existence of progressive neurological defect on examination
In the presence of risk factors, laboratory tests such as blood cell counts, urine tests, and sometimes imaging are necessary. In the absence of risk factors, laboratory tests and imaging are not necessary.

CT scan or plain radiograph of the spine is rarely necessary for the first month of low back pain unless a fracture is present. MRI is a better way to look at soft tissue structures.
Lumbar disc disease
Lumbar disc disease is a common cause of chronic or recurrent pain in the lower back and lower limbs.
Disc disease most often occurs between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae or between the fifth lumbar vertebra and the first sacral vertebra.
They are overweight increases the likelihood of it occurring. Disc herniation is less common in people under the age of 20 and is rare in the elderly. Genetic factors play a role in the development of disc disease in some people.
The pain may be felt only in the lower back or spread to the lower limbs, buttocks.
Sometimes a disc herniation is asymptomatic. On CT or MRI, up to one-third of adults have a disc herniation.
Pain from a disc herniation is made worse by sneezing, coughing, straining when lifting heavy objects or defecating, activity or sitting. In contrast, pain from a narrowed spinal canal gets better by sitting.
An essential test for a doctor to rule out lumbar disc disease is a test called Straight leg raising. During this examination, the patient lies on his back, and the doctor raises his legs directly. Usually, pain does not occur up to 80 degrees, but patients with disc herniation experience pain at a lower angle.
The best method of imaging a disc herniation is MRI. Note that there is no simple relationship between imaging findings and patient symptoms, especially pain. This means that your pain may be severe, but an MRI may show a slight disease, and conversely, an MRI may show a severe disc herniation in a patient with little pain.
If the clinical examination findings are vague, nerve, and muscle tape (EMG and NCV) can be used to identify the nerve root involved.
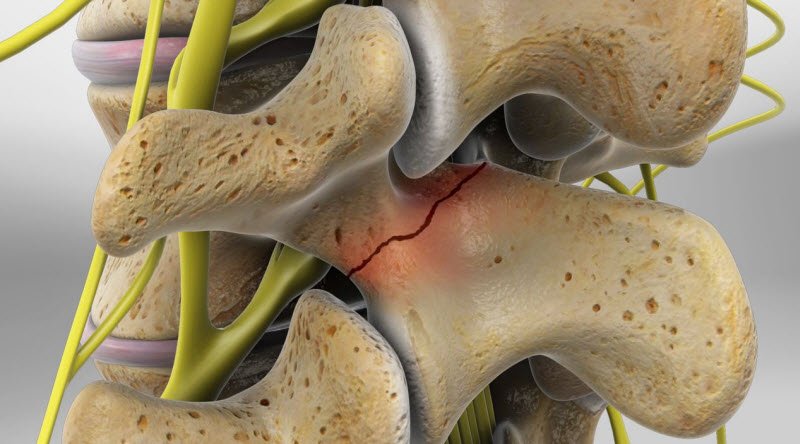
Low back pain due to vertebral fracture
Note that when talking about a vertebral fracture, we are reminded of accidental and severe blows, while minor injuries can also cause various vertebral fractures. For example, adolescent athletes who engage in strenuous exercise that regularly bends and straightens their backs, such as gymnastics, soccer shooting, may experience minor vertebral fractures and back pain in some cases.
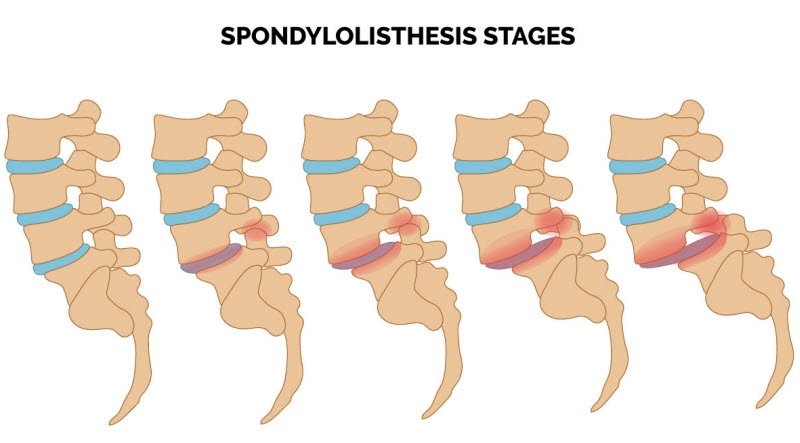
A type of vertebral fracture called spondylolysis is the most common cause of persistent low back pain in adolescents.
Back pain to slip one vertebra on another vertebra
This type of back pain is called spondylolisthesis. In this disease, the upper vertebra usually moves forward on the lower vertebra.
Most of these patients respond to non-surgical treatment, including exercise, medical belts, and painkillers. But sometimes surgery is needed.
Low back pain due to aging
Degenerative spondylolisthesis occurs in people over the age of 50. In these patients, symptomatic spinal stenosis is treated. For this purpose, first weight loss, Williams exercise, and anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended. If the patient does not recover or has severe symptoms of spinal stenosis, surgery may be necessary.
Low back pain due to spinal canal stenosis
These patients develop progressive back, hip, or lower back pain after standing or walking and must stand or bend to reduce pain. However, the pain caused by a disc herniation gets worse with sitting. So they have less pain when shopping on a stationary bike while bending over a shopping cart or when pedaling.
Spinal canal stenosis sometimes causes localized neurological symptoms such as sensory disturbance, weakness, and reflex changes in the lower extremities due to concomitant stenosis of the holes between the vertebrae.
Back pain due to osteoarthritis of the lumbar vertebrae
It occurs in people over the age of 40. These patients complain of back pain and stiffness, and back pain increases with heavy work.
Radiographs show a decrease in intervertebral disc space.
Low back pain due to ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis most often occurs in men under the age of 40 with gradual back pain. Back pain starts at a young age and improves with exercise. Other features of this disease include: nocturnal pain and no improvement in pain with rest – Morning dryness – Increased ESR – Negative RF – Strong association with HLA-B27 – Decreased chest dilatation
In the advanced stages of the disease, the spine fuses and becomes fixed. In the photos taken, the spine is in the form of a tube or a bamboo.
Low back pain due to vertebral infection
The most common cause of vertebral infection; the bacterium is Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcal infection of the vertebrae is seen in patients with endocarditis – hemodialysis, and diabetics, as well as injecting drug users.
Back pain due to vertebral osteomyelitis does not go away with rest. Examination of the vertebrae in the affected vertebrae and the laboratory examination show an increase in ESR. Fever and leukocytosis increase in a small number of patients.
Brucellosis is also a common cause of low back pain.
Low back pain due to osteoporosis
Osteoporotic pressure fractures sometimes cause back pain, although most of these fractures are asymptomatic.
The following treatment methods are useful in the treatment of patients with low back pain due to vertebral fractures:
- Prescribe simple acetaminophen or codeine
- Prescription of calcitonin
- Medical belts
- Back pain due to Paget’s disease
- Paget’s disease increases osteogenic activity in the vertebrae. This condition is often asymptomatic but sometimes causes back pain.
Referral low back pain from internal abdominal disease
The upper abdomen’s diseases cause pain in the lower part of the thoracic vertebrae or the upper part of the lumbar vertebrae.
Diseases of the lower abdomen cause pain in the middle of the lumbar vertebrae.
Pelvic diseases cause sacral pain.
Sometimes pancreatic disease causes back pain.
Back pain due to aortic aneurysm
Sometimes a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm means an abnormal dilation of the aortic vein with back pain. These patients may also have abdominal pain. On examination, the pulsating mass is felt in the abdomen.
The patient is at risk of rupturing the abdominal aortic aneurysm of an older smoker.
Ultrasound, CT, or MRI may help examine suspected cases of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Low back pain due to gynecological diseases
Gynecological diseases such as endometriosis or uterine cancer can cause referred pain in the sacrum.
Typical pain from premenstrual endometriosis occurs and is followed by menstrual cramps.
Back pain caused by kidney and urinary tract problems
Prostatitis or chronic inflammation of the prostate gland – Prostate cancer – Kidney disease can lead to back pain.
Postural back pain
Postural back pain is a vague, diffuse back pain that occurs after sitting or standing for a long time and resolves with rest.
This diagnosis is made after ruling out other causes of back pain.
Doing exercises that strengthen the paraspinal muscles and abdominal muscles are beneficial in some patients.
Treatment of back pain
Most people with acute low back pain recover spontaneously without symptoms of pressure on the nerves.
The doctor should assure the patient that he or she is likely to recover. The patient should be educated about the prognosis, treatment methods, activity modification, and methods to prevent its worsening in the future.
A crucial point in back pain: in general, you should avoid resting in bed or only in cases of severe pain for a day or two. Resting in bed does not speed up the recovery phase. The best activity is walking and returning to normal activities early, and only heavy work should be avoided
Note that doing muscle-strengthening exercises in acute back pain is not beneficial.
Low back pain medications
The first line of drug treatment for pain control is administering acetaminophen or ibuprofen and naproxen, the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Sometimes it is helpful to prescribe muscle relaxants such as methocarbamol.
Long-term use of some muscle relaxants such as benzodiazepines such as diazepam can be addictive, so these drugs’ short-term use is recommended.
Drug-like analgesics such as tramadol are used to treat severe pain or in people who are intolerant to acetaminophen and other painkillers.
Oral or injectable corticosteroids have no place in the treatment of acute low back pain without nerve involvement.
Gabapentin or tricyclic antidepressants have no place in the treatment of acute open back pain.
There is not much evidence about the benefits of physiotherapy, massage, acupuncture, laser or ultrasound treatment, the use of corsets or braces in the treatment of acute back pain.
But what if signs of nerve pressure accompany acute back pain?
Disc herniation is a common cause of acute low back pain with the involvement of nerve roots. Most of these patients improve significantly within a few months, and serial imaging studies show that in two-thirds of patients, the disc herniation resolves spontaneously within six months.
Acetaminophen and naproxen are useful for pain control, but sometimes a short course of a narcotic analgesic is necessary to control severe pain.

Requirements for surgical treatment
Progressive motor weakness on examination or nerve and muscle tape
Very severe and debilitating pain despite appropriate conservative treatment for at least 6 to 8 weeks
Urinary and fecal incontinence
Chronic back pain
Back pain lasting more than three months is called chronic.
Risk factors for chronic low back pain include obesity, female gender, old age, previous history of low back pain, limited movement of the spine, diffuse lower extremity pain, severe mental distress, and low physical activity, smoking
The same treatment is usually used for acute low back pain, but treatment with opioids or muscle relaxants is less useful in the chronic form.
Exercise therapy is one of the main treatments for chronic back pain. Increasing activity tolerance is the first goal, and improving pain is the second goal of exercise therapy.
Some forms of yoga are also helpful.
Prolonged use of massage in chronic low back pain has not been proven.
Acetaminophen, naproxen, and tricyclic antidepressants are used to reduce pain.
Tricyclic antidepressants (drugs such as nortriptyline) effectively reduce chronic low back pain, even in patients with no evidence of depression, but SSRIs (such as fluoxetine) do not have this effect and are only useful in the presence of depression.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is useful in treating chronic back pain.
If chronic low back pain is without symptoms of nerve pressure, the following treatments are not necessary:
- Epidural injection
- Injection into the facet joints
- TENS
- Radiofrequency
- Thermal coagulation