Tuberculosis: Everything about the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that affects the lungs. This known disease can be treated if diagnosed in time.
Tuberculosis = TB
This disease is one of the oldest known human diseases and the most important infectious disease of the present century. The disease has been a significant cause of death worldwide in the past. Over time, the prevalence of tuberculosis in industrialized countries has dropped dramatically due to improved living conditions and antibiotics manufacture. Tuberculosis can be fatal, but in many cases, it can be prevented and treated. In the following, we will be with you to fully introduce this disease, its symptoms, causes, methods of diagnosis, and treatment.

What is tuberculosis?
It is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs, hence the medical name for this disease, pulmonary tuberculosis, but it can affect any part of the body. In general, tuberculosis bacteria grow mainly in the lungs but can infect other parts of the body. Millet tuberculosis is an advanced disease that occurs when bacteria spread through the bloodstream and infect organs beyond the lungs.
People can get the disease after inhaling Mycobacterium tuberculosis. When tuberculosis affects the lungs, the disease is most contagious, but a person becomes ill only after close contact with a person who has the disease. In general, there are two types of tuberculosis, which we will describe below:
Tuberculosis infection (latent tuberculosis):
A person can have tuberculosis bacteria in their body and never show symptoms. In most people, the immune system can contain bacteria that cannot reproduce. In this case, the person will get a TB infection; But it does not have active disease. Doctors refer to this type of tuberculosis as latent tuberculosis. In such cases, the person may never experience symptoms and be unaware of the infection. There is also no risk of transmitting latent TB infection to another person. However, a person with latent TB still needs treatment. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that about 13 million people in the United States have tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis (active tuberculosis):
The TB germ can multiply in a person with active TB and is fully active. This is more likely to happen when a person has a weakened immune system due to illness or the use of certain medications. In general, bacteria multiply in the body of a person with active tuberculosis and cause symptoms. Keep in mind that people with active TB can spread the infection. Tuberculosis, if left untreated, becomes active in 5 to 10 percent of people with the disease. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the disease will progress in 50% of people with the disease within 2 to 5 years after infection.
According to the World Health Organization, TB is one of the top 10 causes of death globally and the leading cause of death due to an infectious agent. According to the World Health Organization, in 2018, nearly 10 million people worldwide were infected with TB, and one and a half million people died from the disease. Statistics show that most of the infected people were from Asia, but the disease was still a concern in many other parts of the world. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2018, doctors identified about 9025 people with tuberculosis.
At present, antibiotic resistance has caused renewed concern among specialists, as some types of the disease do not respond to the most effective treatment options. In these conditions, the treatment of TB becomes tough.
What are the early warning signs of tuberculosis?
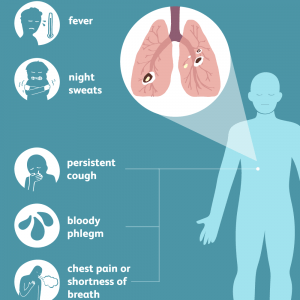
If a person experiences any of the following symptoms, they should be referred to a doctor:
- Persistent and prolonged cough (lasting at least three weeks)
- Sputum and cough with blood
- Decreased appetite and weight
- Feeling weak and tired
- Inflammation in the neck area
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Chest pain
Symptoms of tuberculosis:
The symptoms of this disease will vary depending on whether the person has latent or active TB. In the following, we will refer to the person’s condition after suffering from any of these types of disease:
Latent tuberculosis: A person with latent tuberculosis has no symptoms, and no damage or problems are seen with a chest x-ray. However, a blood test can show that a person has an infection with the disease.
Active tuberculosis: A person with tuberculosis may experience a cough with sputum, fatigue, fever, chills, and loss of appetite and weight. The symptoms of a person with active TB usually get worse over time but may go away on their own and come back.
Outside the lungs:
Tuberculosis usually affects the lungs, but symptoms can also affect other parts of the body. This is more common in people with weakened immune systems. In general, this disease can have the following symptoms:
- Persistent inflammation of the lymph nodes
- stomach ache
- Joint or bone pain
- Panting
- Confusion
- Persistent headache
- Convulsions
Causes of tuberculosis

Mycobacterium TB causes tuberculosis. When a person has pulmonary tuberculosis, coughing, sneezing, spitting, laughing, or even talking, the bacterium can be spread through the air in drops. About a third of the world’s population is infected with the bacterium. However, only about 10 to 20 percent of people with the infection develop active TB. It is essential to know that only people with active TB can transmit the infection. However, most people with the disease will not transmit the bacteria for at least two weeks after receiving proper treatment.
What are the methods of diagnosing tuberculosis?

As mentioned, a person with latent tuberculosis does not experience any symptoms, but the infection can be seen in various tests, such as a blood test. This condition is more common in people who have been exposed to the following conditions:
- Spending time with someone who is at risk for TB
- Has lived for some time in a country with a high incidence of tuberculosis
- Working in an environment where tuberculosis may be present
The doctor first asks the person about their symptoms and medical history and performs a physical exam that includes examining the lungs’ sound and the swollen lymph nodes’ condition. Note that two tests can show the presence of TB bacteria, which we will mention below:
- Skin test
- blood test
Tests cannot show whether the disease is active or latent. To diagnose active TB, your doctor may recommend a sputum test and chest x-ray. Keep in mind that all people with TB need treatment, regardless of whether the infection is active or latent.
Treatment of tuberculosis:

If the disease is diagnosed in time, and the person receives appropriate antibiotics prescribed by a doctor, it can be treated. Note that the appropriate type of antibiotic and the length of treatment depend on the following:
- Age and general health of the person
- Active or latent type of tuberculosis
- The site of infection
- TB strain resistance to the drug
Treatment for latent tuberculosis can vary, meaning your doctor may prescribe antibiotics once a week for three months or every day for nine months. In contrast, treatment for active tuberculosis may require multiple medications for 6 to 9 months, with initial treatment options including isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. Keep in mind that treatment can be more complicated when a person has a drug-resistant TB strain.
Even if the symptoms go away, it is essential to complete a full course of treatment. If a person stops taking their medication early, some bacteria will survive and become resistant to antibiotics. In this case, the person may develop drug-resistant tuberculosis, but depending on the body’s parts affected by the disease, your doctor may also prescribe corticosteroids.
When should I see a doctor?
TB can be treated, but if left untreated, it can be life-threatening. Also, latent tuberculosis can become active tuberculosis if a person does not take preventive measures for treatment. In general, anyone experiencing symptoms of the disease should see a doctor for testing. Also, anyone suspected of having the disease should seek medical advice.
Ways to prevent tuberculosis
Here are some ways to prevent TB:
- Timely diagnosis and treatment
- Stay away from other people until there is no longer a risk of infection
- Use a mask and cover your mouth
Tuberculosis vaccination:
In some countries, children receive tuberculosis vaccination as part of a regular vaccination program, which may also be recommended for medical staff, doctors, and nurses because they are at high risk for TB. Still, experts in the United States do not recommend the TB vaccine for most people unless there is a high risk of getting TB. Some of the reasons for this decision include the low risk of infection in the country and the possibility of vaccine interference in any future TB skin test. (Moderna Corona Vaccine And Efficacy 94.5%)
Risk factors for tuberculosis in individuals:
People with weakened immune systems are more likely to develop active TB. The following are some of the factors that can weaken the immune system.

AIDS: Doctors recognize tuberculosis in people with AIDS as an opportunistic infection; This means that a person with AIDS has a higher risk of developing TB and more severe symptoms than a healthy immune system. TB treatment can be complicated for a person with AIDS, but a doctor can provide a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both issues.
Smoking: Smoking and cigarette smoke increases the risk of TB. These factors also make the disease more difficult to treat and increase the likelihood of recurrence after treatment. Quitting smoking and avoiding contact with smoke can significantly reduce the risk of TB.
Other conditions
Other health issues that weaken a person’s immune system and can increase the risk of tuberculosis include:
- Low body weight
- Diabetes (Diabetes: Everything About The Symptoms And Treatment Of Diabetes)
- Silicosis
- Severe kidney disease (Common Kidney Disease In Women + Prevention And Treatment)
- Neck and head cancer
Also, some medical treatments, such as organ transplants, block the immune system’s proper functioning. Spending time in a country where tuberculosis is expected can also increase the risk of developing the disease.
What are the complications of tuberculosis?
TB can be fatal if left untreated. If the infection spreads throughout the body, it may cause problems with a person’s cardiovascular system and metabolic function. It can also lead to sepsis, a severe, life-threatening infection.
An Overview of Tuberculosis:
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), tuberculosis is one of the deadliest diseases globally, with approximately 1.3 million deaths associated with it worldwide in 2017. It is also the leading cause of death among people living with HIV. However, the CDC report shows that the incidence of TB in the United States has been steadily declining since 1993. The incidence of tuberculosis in 2018 was about 2.8 cases per 100,000 people, which is the lowest rate reported in this country.
In 2016, doctors confirmed 528 TB-related deaths in the United States, up from 470 in 2015. The CDC estimates that up to 13 million people in the United States may have latent TB, with 1 in 10 developing active TB. Note that the risk of developing latent TB to active TB is higher among people with weakened immune systems, such as people with HIV and people with cancer or organ transplants. Be sure to see your doctor if you notice TB symptoms or contact someone who has active tuberculosis. These conditions can be treated, especially when a person is diagnosed early.
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that can be transmitted between people through the air and is associated with a wide range of symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and a severe cough. If a person with the disease is not treated correctly, active TB infection can be contagious and life-threatening. However, most cases of TB are treatable, especially if diagnosed early.
Latent TB is not contagious, but it can eventually become active TB. Doctors treat latent or active tuberculosis by prescribing a long course of antibiotics, and people with active TB usually feel better after a few weeks of treatment. Note that anyone at risk for tuberculosis or its symptoms should see a doctor as soon as possible.