The symptoms of kidney stones and how to treat them +video
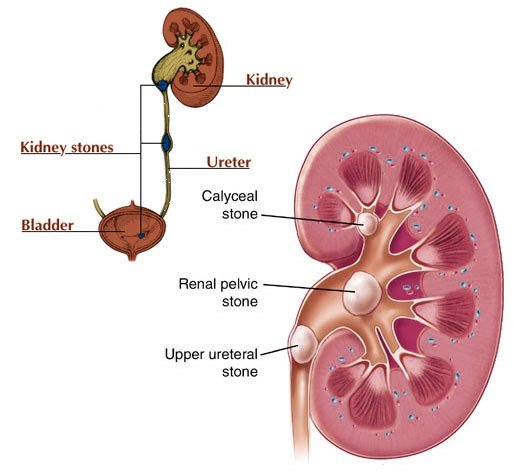
The symptoms of kidney stones and how to treat them : Kidney stones are a collection of minerals and salts that can move or stay together throughout the urethra and cause infection or complications when formed inside the kidneys. They are different and can even grow several centimeters.
Naturally, the prevention of kidney stones requires some changes in our lifestyle and habits. For example, drinking water is necessary to prevent the formation of kidney stones because when your body is dehydrated, your urine excretes more minerals—the higher your urine concentration, the greater your risk of developing kidney stones. Choosing a low-sodium diet can also help prevent kidney stones.

signs of kidney stones
Heartburn, back, and side pain
Kidney stone pain is compared to labor pain. This movement of the stone puts pressure on the kidneys.
The pain can start suddenly and spread to your back.
Blood in the urine
In this case, the urine is usually pink, brown, or red. Sometimes blood cells are not visible to the human eye, so it would be better to ask your doctor.
Intermittent pain during urination
When the stone reaches the bladder, severe pain and tingling are often confused with urinary tract infections. Irregular urination is the main sign of kidney stones.
Stinky urine
Stinky urine can be a sign of an infection in the urinary tract or kidneys.
Inability to control the bladder
Obstruction caused by kidney stones can stop the flow of urine. If you can not urinate, go to the nearest medical center.
Nausea or vomiting
kidney stones normally are formed through the connections between the gastrointestinal tract and the kidneys, and this problem will cause nausea, fever, and chills; in this case, you should go to the nearest medical center ASAP!
Symptoms of kidney stones vary by age and gender due to differences in the urinary tract

Men:
Groin or abdominal pain
stomach discomfort
Women:
Pain or itching in the penis
Secretions
Menstrual cramps
children:
Restlessness
Differences in urine color and frequency
Causes of kidney stones
Kidney stones often have no definite cause, but several factors may increase the risk.
Kidney stones form when urine contains extra crystalline substances such as calcium, magnesium, and uric acid than fluids in the urine. The urine may also lack substances that prevent the crystals from sticking together, which will make an ideal kidney stone environment.
types of kidney stones
Knowing the type of kidney stone will help determine the cause, and you may have more clues as to how to reduce your risk of developing kidney stones.
calcium kidney stones
Calcium stones are in the form of calcium oxide. Some fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts and chocolate, have a high oxalate content.
Dietary factors, high levels of vitamin D, intestinal surgery, and several metabolic disorders can increase calcium concentration in the urine.
Calcium stones may also form in the form of calcium phosphate. It may also be associated with severe migraine headaches or with the use of certain epileptic drugs.
struvite stone
Struvite stones form in response to an infection, such as a urinary tract infection. These stones can grow and even overgrow.

Uric acid stones
Uric acid stones can form in people who do not drink enough fluids or excrete many fluids, people who have a high protein diet, and those who have gout. They are more likely to get this type of kidney stone.
Cystine stones
These stones form in people with an inherited disorder and cause the kidneys to excrete too much amino acids.
Factors that increase the risk of kidney stones include
family history
If someone in your family has kidney stones, you are more likely to develop stones. If you have had one or more kidney stones before, you are at risk of getting them again.
Dehydrated
Not drinking enough water can increase the risk of developing kidney stones. People who live in hot climates or sweat a lot may be at higher risk than others.
Special diet
Having a diet high in protein, salt, and sugar may increase the risk of some types of kidney stones. Too much salt in your diet increases the amount of calcium and the kidneys and significantly increases the risk of developing kidney stones.
Obesity
High body mass index, high waist size, and weight gain are associated with an increased risk of kidney stones.
Gastrointestinal diseases and surgery
Gastric bypass surgery, an inflammatory bowel disease, can cause changes in the digestive process that affect the absorption of calcium and water and increase the number of stones in the urine.
Diagnosis of kidney stones
If your doctor suspects you have kidney stones, you should have the following tests and diagnostic tests:
blood test
Blood tests may show large amounts of calcium or urea acid in the blood. Blood test results help monitor kidney health and other diseases.
Clinical urine tests
A urine test collected over 24 hours may indicate that you have consumed too much stone formation minerals.
For this test, your doctor may ask you to have two urine tests for two consecutive days.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging from inside the urinary tract may show kidney stones.
An option is to use a plain X-ray, which may not show small kidney stones.
The second option is high-speed computed tomography (CT), which shows even small stones.
kidney stones treatment
The treatment for kidney stones varies depending on the type of stone and the cause.
Small stones with the least symptoms:
Most small kidney stones do not require invasive treatment, and you can get rid of them by doing the following tips:
drinking water :
Drinking 1.9 to 2.8 liters of water a day may help clear the urinary system so that you have clear urine.
Sedatives
Passing a small stone can cause discomfort. Your doctor may recommend medications such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or naproxen sodium to relieve mild pain.
Medical treatments
Your doctor may prescribe medication to help eliminate kidney stones. These drugs, known as alpha-blockers, relax muscles, and reduce pain.
Parathyroid glands
some kidney stones can not be treated with the usual methods due to their large size and bleeding danger, or even urinary tract infection, so that you may need more extensive treatment in these cases.
Treatments may include the following:
Use sound waves to break the stones. Depending on their size and location, your doctor may recommend a Lithotripsy procedure for some kidney stones.
This treatment causes the stones to break into small pieces to pass through the urethra. This process takes about 45 to 60 minutes and can cause moderate pain, so you may be taking sedatives or anesthetics to relax.
ESWL can cause blood in the urine, bruising on the back or abdomen, and bleeding around the kidneys and other organs.
Use a scope to remove stones:
To remove a smaller stone in the bladder or kidney, your doctor can use a camera-equipped urethroscopy to pass through the bladder canal. When a stone is seen, special tools can remove the stone or crush it to pass through the urine. You may need general or local anesthesia during this procedure.
Parathyroid gland surgery:
The bladder glands make some calcium phosphate stones. When these glands produce too much parathyroid hormone, the amount of calcium can rise too high, and kidney stones may form.
Hyperparathyroidism occurs when a small, benign tumor forms in one of your digestive glands. Stopping the growth of the gland prevents the formation of kidney stones. Or your doctor may recommend treatment that causes the parathyroid gland to produce more hormones.
Also Read:
The causes and symptoms of kidney protein excretion +video
everything about kidney? What are the functions of the kidneys ?