Risk of radiology for pregnant women
Pregnancy is one of the most sensitive periods for pregnant women and the fetus, so during this period, women should take extra care of themselves and avoid activities that endanger their health and that of the fetus. Radiology is one thing that a doctor uses to diagnose, but radiology during pregnancy is dangerous for women and their fetuses.
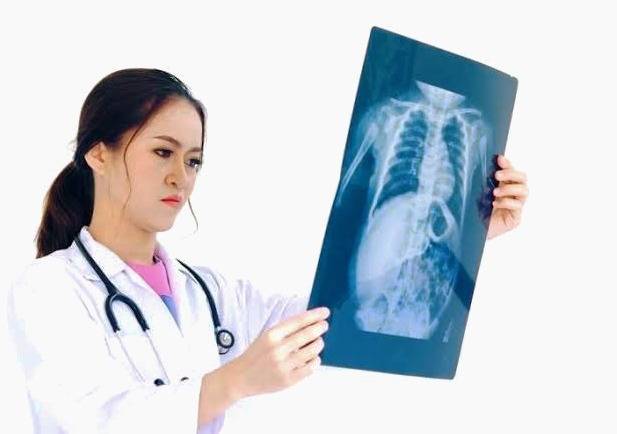
Perform radiology for pregnant women
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation that can pass through solid objects, including the body. High-density X-rays penetrate various items. In medicine, X-rays are used to see images of bones and other body structures.
For X-rays, a part of the patient’s body is exposed to radiation. When X-rays pass through the body, the radiographs look like black and white shadows depending on the tissue that the X-rays pass through. In most cases, the radiology is of the hands, feet, head, and teeth. , Is located in the chest and does not affect the genitals.
What are the complications of radiology for pregnant women?
Lack of knowledge about pregnancy and radiology can have adverse effects on the fetus. But in general, the information obtained from radiology is more important than its potential risk.
Abortion:
Abdominal radiology in pregnancy due to radiation can lead to miscarriage or adverse effects on the developing fetus.
Genetic problems:
High-dose radiation to pregnant women undergoing radiology can cause genetic problems and reproductive risks in the fetus.
Mental and learning disabilities:
In the second and eighth weeks of pregnancy, the risk of fetal growth retardation or congenital disabilities increases, and radiation exposure after the eighth week increases the risk of mental retardation and learning and cancer risk.
How much radiation harms the fetus?
When calculating the X-ray dose, various factors must be considered, including the type of diagnostic test, the type and life of the device, the distance of the target organ from the radiation source, and the thickness of the organ through which the radiation passes.
Radiation is measured in radiology in units called MGY. Doses higher than 100 MGY may harm the fetus. But the radiation used in the hospital is much weaker than this.
For example, the amount of radiation in dental radiology is meager and safe. The usual dose of radioactive radiation has fewer side effects.
Radiology Which organ is at risk?
Chest radiography is one of the most common radiographic images during pregnancy. In this radiograph, the fetus is exposed to very little radiation.
Abdominal radiography at higher doses is more dangerous for pregnant women and the fetus because it is exposed to direct radiation.
Exposure to radiation with a pregnant mother in the 8th to The 15th week of pregnancy increases the fetus’s risk of mental retardation. At higher doses, mental retardation has not been seen in pregnant mothers’ fetuses under eight weeks or more than 25 weeks.
If you are pregnant, follow these tips:
If you are pregnant, tell your doctor about your condition before having radiology. Depending on the circumstances, it may modify or reduce the amount of radiation.
If your baby needs radiology and you are pregnant, do not stay there.
The lead coating should be used for the image, and radiology should be performed with a limited beam and increased tube distance.
Ask your doctor to use other X-ray imaging techniques.
As a pregnant woman, if you are exposed to X-rays in the workplace, talk to your employer about protecting yourself and your baby.
If you find that you are pregnant after a radiograph and are concerned about your fetus’s health, ask a specialist doctor to determine the amount of radiation emitted. More than five units of radiation are dangerous to the mother’s body. Still, in most cases, less than this amount of radiation on The body emits, so do not worry.
If you do not use contraception and do not know if you are pregnant, the best time to get non-emergency radiographs of the pelvis and abdomen is the first 14 days of pregnancy. Ten days after the onset of menstruation until ten days later, you can safely take radiographs.
Risk of radiology during lactation
Exposure to X-rays while breastfeeding is safe. If breastfeeding women need a mammogram because of radioactive isotopes, they should advise their doctor to stop breastfeeding for a short time.
also read:
Essential tips and knowledge for a 40-day-old child
The benefits of dates in pregnancy and how they can facilitate childbirth










