What are the risks associated with heart balloon surgery?
The most common form of heart disease is coronary artery disease (CAD). Atherosclerosis or atherosclerosis is often responsible for this condition.
Fat builds up in the arteries of the heart, causing atherosclerosis. Plaque narrows the arteries, which makes it difficult for blood to flow to the heart. As the obstruction worsens, blood flow to the heart slows down, resulting in angina. During this time, a blocked or narrowed artery can cause a heart attack.
Angina pain caused by coronary artery disease can be relieved with several medications. Due to the fact that drugs cannot clear blocked arteries, severely narrowed coronary arteries require more treatment to reduce the risk of heart attack. Percutaneous arterial interventions, such as angioplasty or stenting, are required in these situations.
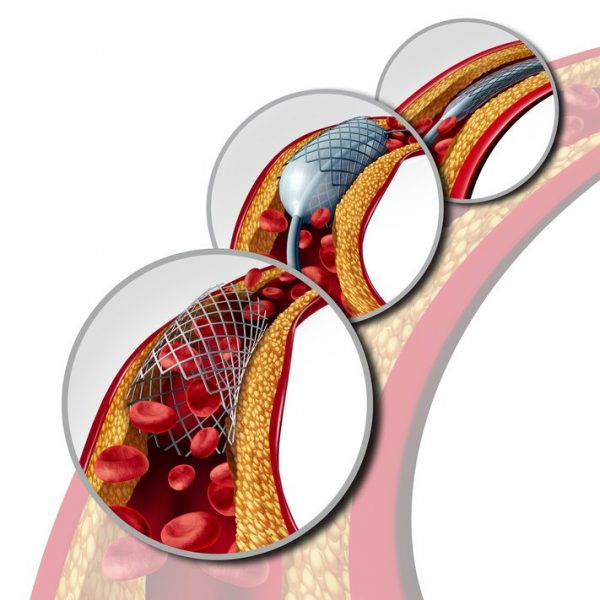
How does a balloon angioplasty work?
Angioplasty (heart balloon) is performed by cardiologists to widen narrow coronary arteries. A catheter contains a small balloon at its tip, which is used by these specialists. The balloon is placed at the open artery blockage site to flatten or compress the plaque on the artery wall.
Other parts of the body can also be treated with balloon angioplasty.
To open narrowed carotid arteries, doctors perform carotid angioplasty. The carotid arteries carry blood to the brain. When the carotid arteries become blocked, the brain does not receive enough oxygen, resulting in stroke.
A balloon angioplasty can also be performed on the aortic artery (the artery leading from the heart), the iliac (inside the pelvis), the thigh (above the thigh), the fallopian tube (behind the knee), and the peroneal bone (lower leg).
Heart stents: what are they?
A stent is a small metal device. In coronary arteries, a stent acts as a supporting structure or scaffold and keeps the vessel open. Stents increase blood flow to the heart and reduce angina pain by keeping arteries open.
A heart stent is usually used during the ballooning procedure. A stenting procedure is also performed in about 80% of balloon angioplasty patients.
In addition to balloon angioplasty, doctors today use stents on different parts of the body as well. The carotid arteries of the neck, the aorta, and peripheral arteries in the legs can be treated with stents.
How does a balloon angioplasty work?
A cardiac catheterization laboratory performs these procedures. Before surgery, patients are advised not to eat or drink after midnight because it can affect their blood sugar levels. Talk to your doctor about food and insulin if you have diabetes.
Any medications or supplements the patient is taking should be discussed with their doctor. When a person is taking antiplatelet or blood thinners, this is especially true.
To anesthetize the catheter entry site, anesthetic is injected into the area with a needle, followed by a small incision. Doctors use a unique needle to pierce the artery when inserting the catheter.
Catheters are usually inserted into an artery in the leg, arm, or wrist. Leg arteries are often used by doctors. Radial artery access (wrist) is becoming more common.
The doctor inserts the catheter gently into the artery and then into the heart. Video monitors, such as TV screens, are used to monitor trends.
During coronary angiograms, a harmless dye is injected into the blocked artery, and the doctor takes a picture of the coronary arteries. In an angiogram, the doctor can see the size and location of the blockage.
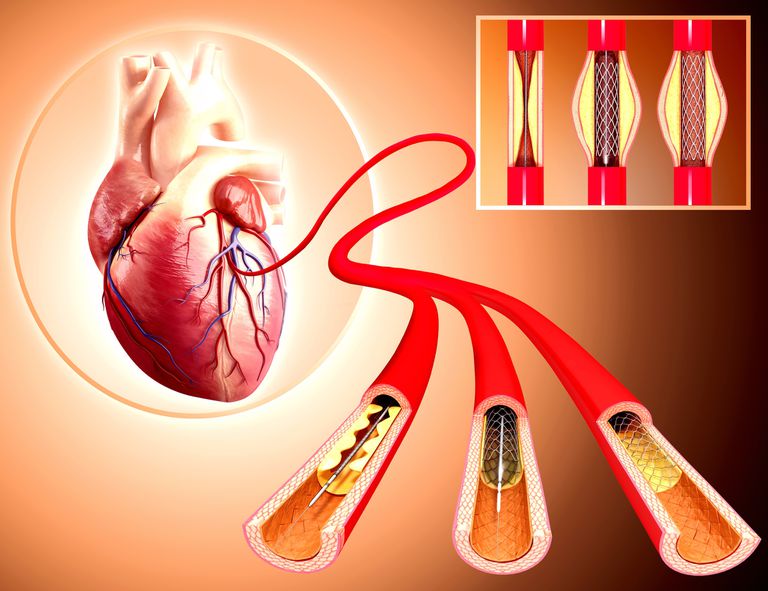
In order to reach the obstruction, the doctor inserts a guided wire device through the same artery in the leg. The balloon swells once it reaches the blockage site. After the balloon expands and presses against the plaque, it empties. The balloon may be inflated several times by the doctor. The catheter, guided wire, and empty balloon are removed from the patient after the heart ballooning process has been completed.
Stents are placed at the catheter’s tip and on the balloon when doctors plan to insert them into an artery.
As the catheter enters the occlusion site, the balloon expands and expands the stent. The balloon is emptied after the stent is opened. Following the removal of the catheter, guided wire, and empty balloon, the stent is left open to keep the artery open.
Pressure is applied to the area where the catheter is inserted to prevent bleeding, and it also serves as a dressing area.
After surgery, most patients stay in the hospital for about 1.5 to 2.5 hours. Until the sedative effect wears off, the person may feel drowsy. Blood pressure and heart rate are monitored by nurses.
After balloon angioplasty, what happens?
After surgery, you should drink plenty of fluids and refrain from driving, bathing, or smoking for 1 or 2 days. During the first two days after surgery, sitting or walking for long periods of time should be avoided.
For 30 days after receiving a stent, you should refrain from strenuous activity. Aspirin should be taken for the rest of your life, whether you had angioplasty with or without a stent. After stenting, the patient should take antiplatelet or blood thinners for a year or more. You will be told when and how to take these medications by your doctor.
The condition known as spinal stenosis occurs in about 35 to 40 percent of patients with a heart balloon. In the first six months after a heart balloon, recurrent stenosis usually occurs. A stent can also be removed, and about 20% of patients with stents regenerate their arteries. Restenosis may require a heart balloon or other stenting.
Is it possible to prevent spinal stenosis?
As a result of angioplasty and stenting, doctors are constantly seeking new ways to prevent the arteries from closing again. New types of stents have been developed in recent years. Many of these cases are impregnated with drugs that prevent the arteries from closing again. Stents implanted into the body slowly release their drugs into the tissue around them to prevent them from narrowing.
Blood-thinning drugs are impregnated into other stents to prevent blood clots. In recent years, researchers have developed stents that dissolve in blood vessels over time. The stents open the artery, have the same results as metal stents, and reduce the risk of re-narrowing.
Also Read:
How to diagnose coronary heart disease?