Everything about Spinal cord tumor
Spinal cord tumor is one of the tumors that affect people of different ages, and the origin of this tumor goes back to cancerous masses that exist in other parts of the body. Like other tumors, there are many ways to treat this complication.
Tumors or cell masses
In general, tumors can grow all over the body. Unfortunately, cancer is not easily detected, and therefore, the abnormal growth of any mass in the body is a form of cancer.
The prevalence of brain tumors is much higher than spinal tumors, classified according to the type of cancerous tissue and its location.
Tumors are divided into two categories:
- Benign (non-cancerous)
- Malignant or metastatic (cancerous)
When masses grow on the spine, spinal cord, bones, and nerve roots, they form spinal tumors.
Sometimes tumors that form in a person’s body first originate outside the spinal cord and gradually spread to the lower back and spinal cord. In other words, some cancerous tissue that forms outside the spinal cord can also grow around the spinal cord and may also penetrate the vertebrae, causing pain and contraction of the vertebrae.
The second area is the spread of cancerous tissue in the spine. Therefore, tumors can put pressure on the spinal cord or epidural space and soft tissues.
Types of spinal tumors
All spinal cord masses can lead to nerve problems, pain, and in some cases, paralysis.
There are several types of spinal tumors, listed below:
Spinal tumors (extracorporeal tumors)
Spinal tumors are divided into two categories:
- Metastatic tumors
- Precancerous or primary tumors
- Tumors outside the body involve the spine.
Most tumors that form in the spine are metastatic. Thus, the main tumor is made in another part of the body and transmitted to the spine, released through the bloodstream.
Most metastatic tumors in men are formed by the lungs and prostate and occur in women due to lung and breast tumors, and there are different types of malignant and malignant bone tumors.
Benign tumors include giant cell tumors, osteoblastoma, and osteoma.
Malignant tumors of the spine also include chordoma, Ewing sarcoma, osteogenic sarcoma, chondrosarcoma.
Intraoral tumors (intrauterine tumors)
- Nerve sheath tumors
- Meningioma
- Schwannoma
- Neurofibroma
These types of spinal tumors are located inside the perineum or outer layer of bone. However, they are outside the spinal cord itself and are, in fact, the main cause of tumors formed in the spinal cord, neurological tumors, and meningiomas.
Meningioma usually forms in middle-aged women and is classified as a benign tumor. This type of tumor grows inside the pubic area and is the perineum, a thin membrane that encloses the spinal cord and spinal fluid.
Schwannoma and neurofibroma tumors, like meningiomas, are benign nerve fibers. The nerve roots of the body, leaving the spinal cord, cause the formation and growth of schwannoma and neurofibroma masses.
Tumors within the spinal cord tissue
Intrathecal tumors are formed by supporting cells, astrocytoma, ependymoma, and ependymoma tumors common in adults and astrocytoma tumors in children.
Von Hipple-Lindau disease (VHL)
It is an inherited disease in which primary tumors form in the uterus or cervix and spread to the kidneys. Fortunately, this type of disease is benign.
Cause of spinal tumor
The main cause of spinal tumors is mostly due to genetic defects. But as we said, in some cases, cancer cells in the lungs, chest, and kidneys can spread to the spine over time.
Another major cause of mass formation is the overgrowth of cancer cells in the spine’s nerves, bones, and cartilage. In addition, exposure to radiation and chemicals can cause this complication.
Symptoms of spinal tumors
Symptoms of spinal cord mass depend on factors such as their type, size, and growth.
Spinal cord mass, pain in the neck and back, changes in urinary and intestinal habits, and neurological problems such as weakness and numbness in the arms and legs are the most common symptoms.
These do not include all symptoms. In the following, we will discuss all the symptoms of a spinal cord tumor.
Clinical signs of spinal cord tumor:
- Inability and lack of coordination in walking
- Increased body temperature
- Feeling of pain in the lower back and neck
- Exacerbation of knee and ankle muscle cramps
- Lack of bladder and anal control
- Incomplete paralysis
- Sciatica
- The feeling of frequent pain and its intensification at night
- Anorexia
- Sudden weight loss
- Sensory disturbance in the limbs
- Stimulation of the soles of the feet. Normally, the thumb jumps down when stimulated.
Hoffmann reflex; In this reflex, contact with the middle finger causes the index finger to bend.
Importantly, for people with cancer in other parts of the body, the onset of spinal pain can be a serious warning sign of a fracture in their spine due to a metastatic tumor.
Ways to diagnose a spinal tumor:
An international standard system, known as the staging system, classifies tumor types based on size, lymph nodes involved, and the likelihood of metastasis.
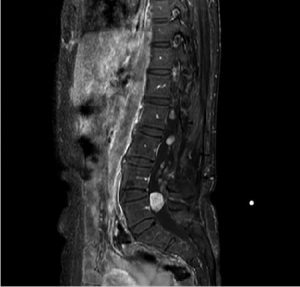
The stages of the disease examination process include ultrasound, MRI, CT scan.
Also, the most accurate type of test is the MRI test, which uses venous gadolinium. In other words, a special dye is injected into the spinal cord, which lightens the body’s tumors.
This test provides an image of the spine and spinal cord, but the details of the image of the spine are not as accurate as a CT scan.
A specialist uses diagnostic tools such as angiography, myelography or X-rays, biopsies or blood samples, and tests to provide quality treatment. It is important to know that blood tests can only diagnose the disease in certain cases.
Spinal cord tumor surgery:
To choose the right treatment, the doctor must be aware of the patient’s age, clinical history, size, and type of tumor. The most difficult step in the treatment process is to diagnose the patient’s tumor type, especially when we face vertebral fractures due to infection and disease.
In any case, spinal tumors must be removed to prevent infection and other areas of the body.
For different types of spinal tumors, treatment options are offered specifically by your doctor. In the following, we will express them.
Preliminary tumor surgery
As mentioned, primary tumors form inside the spinal cord, and the best treatment for primary tumors is surgery and complete removal from the body. Such surgery usually prevents the disease from spreading to other areas and maintains nerve function in the spinal cord.
Neurophysiological methods such as SSEP and MEP are used to operate on primary tumors.
Treatment of spinal tumors:
Tumors of the spine are bony and metastatic.
In people with metastatic tumors, treatment is done separately through radiology, chemotherapy, and surgery.
Radiation therapy is commonly used to reduce back pain. This treatment puts a lot of pressure on the tumor cells and, as a result, the size of the tumor becomes smaller.
When your doctor diagnoses a tumor in your body that puts pressure on your spine and upsets it, they will use surgery to treat it.
In this surgery, part of the vertebrae that are involved with the tumor is removed. Then, when the problem is resolved, they use bone and artificial metal implants to restore the spine’s stability.
Sometimes the epididymis at the end of the large species cannot be completely removed from the body because it is attached to the nerve fibers of the spinal cord, so the healing process is completed with the help of radiation therapy.

Complications after spinal cord tumor surgery:
Today, the risk of paralysis after lumbar surgery is less than 5%.
One of the complications of spinal cord surgery is altered nerve function. Your doctor will recommend a physiotherapist to correct this change.
Types of spinal tumors, what is the cause of spinal tumors, what are spinal tumors
Another complication of surgery is spinal fluid leakage through the incision. This complication occurs in people who have had radiation therapy before surgery. Fortunately, infection and postoperative bleeding are also sporadic.