Dizziness due to high blood pressure
Frequent confusion can significantly affect a person’s life. However, dangerous and sudden dizziness is sometimes a sign of a life-threatening problem.
Symptoms of dangerous dizziness
People who are confused may describe a wide range of emotions, including:
- False feeling of movement (dizziness)
- Feeling light or faint
- Instability or loss of balance
- Feeling suspended or heavy head
These feelings can start or get worse with walking, standing, or moving the head. Dizziness can be accompanied by nausea, or it can be so severe and sudden that the person needs to sit or lie down. Confusion can last from a few seconds to a few days and increase again.
When should we see a doctor?
Have you ever wondered what dangerous vertigo is and you should see a doctor for it? Generally, you should see a doctor if you experience recurrent or unexplained dizziness.
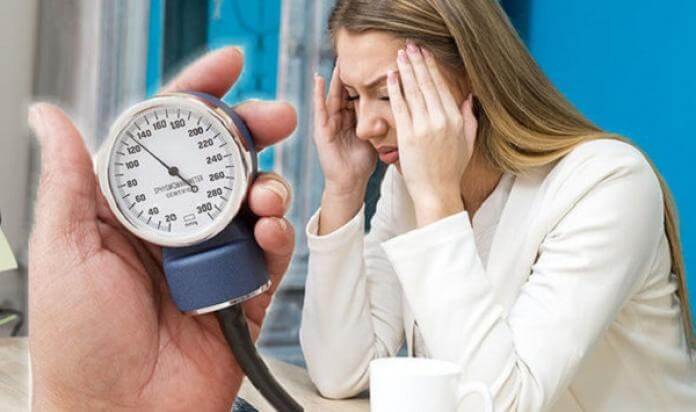

If a person has recently had severe dizziness with any of the following, they should seek medical attention:
- Severe and sudden headache
- Chest pain
- Breathing problems
- Numbness or paralysis of the hands or feet
- Loss of consciousness
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat
- Confusion or intermittent talking
- Persistent vomiting
- Convulsions
- Sudden change in hearing
- Weakness or numbness of the face
The cause of vertigo has many factors, including inner ear disorder, motion sickness, and drug effects. Sometimes the disease is caused by an underlying illness such as poor circulation, infection, or injury.
What are the symptoms of dizziness?
Feeling confused and the stimuli that provoke it are signs of possible factors. Also, persistent confusion and other symptoms can help discover the cause of persistent dizziness.
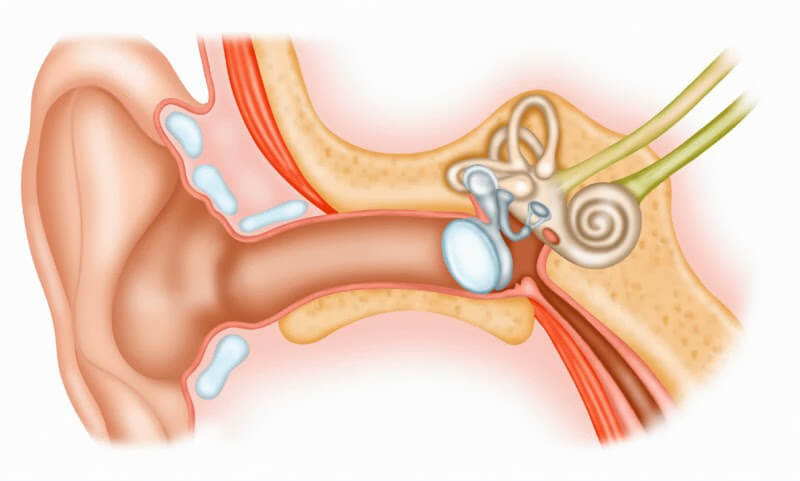
Eyes: They help determine the position of the body in space and how it moves.
Sensory nerves: They send messages to the brain about the positions and movements of the body.
Inner ear: Includes sensors that help detect gravity and reciprocating movements.
Dizziness is a feeling of false rotation or movement around a person. In inner ear disorders, the brain receives messages from the inner ear that do not match the statements’ eye and sensory nerves. Dizziness is the result of the brain trying to organize this information mismatch.
BPPV: This condition can cause a person to feel a strong, brief, false rotation or movement. Attacks of this confused head begin with a rapid change in head movement. Lying in bed, sitting, or hitting your head are some of these quick changes. Dizziness is the most common cause of dizziness.
Infection: Viral infection of the atrial nerve can cause severe and persistent dizziness.
Meniere’s disease: This disease involves excessive accumulation of fluid in the inner ear. The condition is characterized by sudden attacks of dizziness that can last for several hours. You may also experience hearing loss, ringing in the ears, or feeling full.
Migraines: People with migraines can feel dizzy even if they do not have severe headaches. Such dizziness attacks can last from a few minutes to a few hours, and in addition to the headache is also associated with sensitivity to light and sound.
Circulatory problems that cause dizziness
If the heart does not pump enough blood to the brain, it may experience dizziness, weakness, or imbalance. Its factors also include the following:
Low blood pressure: A severe drop in systolic blood pressure can lead to lightheadedness or fainting. This condition can occur after getting up quickly or getting up quickly. This is called orthostatic hypotension.
Neurological diseases: Some neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease or MS, can lead to a gradual loss of balance.
Medications: Confusion can be a side effect of some medications. These include anticonvulsants, antidepressants, sedatives, and painkillers. In particular, antihypertensive drugs can cause fainting if they lower blood pressure too much.
Anxiety Disorders: Some anxiety disorders can cause a feeling of lightheadedness or boredom, often known as confusion.
Low iron levels (anemia): If a person has anemia, other signs and symptoms accompanied by confusion include fatigue, weakness, and paleness.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia): This condition usually occurs in people with diabetes who take insulin. Dizziness (lightheadedness) can be accompanied by sweating and anxiety.
Overheating and dehydration: If a person works in hot weather and does not consume enough fluids, they may feel dizzy due to overheating and dehydration. This is especially true when a person is taking certain heart medications.
Factors that can increase the risk of confusion include:
Age: Older people are more likely to develop conditions that confuse, especially imbalance. Also, these people are more likely to take medications that confuse them.
History of dizziness: If you have had dizziness in the past, it is more likely to occur in the future.
Complications of vertigo
Confusion can increase the risk of falling and injuring yourself. Experiencing disorder while driving or operating heavy machinery can increase the likelihood of an accident. Also, if a confusing illness is not treated, there is a possibility of long-term complications.
also read:
25 facts you need to know about sleep