Carpal tunnel syndrome; The most common disease lurking in computer users
If you work with a computer for more than 5 hours a day, you are more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome. Follow this article to get acquainted with this disease and its prevention and treatment methods.
It started early with very simple and superficial pain. It was as if my wrist was tingling, and I was constantly twisting it to relieve the pain. That’s why it was easy to ignore. This pain should be like any other everyday pain. But the pain got worse, especially when I bent my wrist. A little later, I realized that I could no longer straighten my hand completely. As I tried to straighten my arm, I noticed a very small angle on my wrist. Exactly the angle required when typing.
Eventually, the pain became so severe that I went to the hospital and showed my hand to the orthopedist. He bent my wrist and said: Does your hand hurt? I said, “Too much,” and then that day, I heard a response that I did not know would be a terrible nightmare for me. “You must act as soon as possible;” Because you have carpal tunnel syndrome. “
I was admitted for surgery a few days later. Because I was treated too late, my wrist became more severe, and to return to normal, in addition to carpal tunnel release surgery, a 10 cm platinum was twisted into my wrist bone. I did a lot of things during my life. But carpal tunnel surgery was the most painful.

Wrist tunnel syndrome lurks in typists, musicians, and assembly line workers
Even after the surgery, it was very difficult for me to tolerate such a large amount of platinum. When it was cold, my hand hurt so much that I could not move it easily. It took me a year to get rid of platinum.
After ten years, my wrist still hurts. Especially when I hold the phone or the game handle for a long time. After surgery, I always use the medical keyboard and rest my hands while typing. I advise all people who work a lot with the keyboard to use a medical keyboard and take the symptoms seriously.
This was the true story of a man who developed wrist tunnel syndrome at 20 and never recovered because he had long ignored its symptoms. This syndrome is very common in people who do a lot of repetitive movements, such as typists and musicians, but most assembly line workers and the symptoms may be so mild for a long time that we do not even suspect it. Burning fingers is a sign of this serious problem.
The sooner you notice the symptoms of this disease and try to treat it, the better your chances of complete recovery. Please read this article to know about carpal tunnel syndrome, its symptoms, and methods of prevention and treatment.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
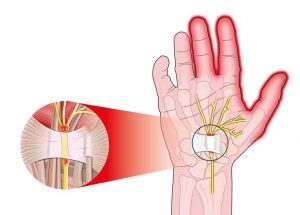
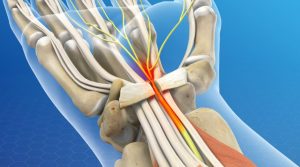
Wrist tunnel syndrome is one of the most common peripheral neuropathies in which the median nerve that runs from the forearm to the palm is compressed in the wrist area. The carpal tunnel or atrium of the wrist is a very narrow passage three centimeters in diameter and inflexible, consisting of ligaments and bones of the end of the hand. It houses the middle nerve and the flexor tendons of the fingers.
Because of this middle nerve can feel the middle, thumb, and part of the ring finger (but not the little finger) inside the thumb and forefinger. This nerve also controls some of the small muscles under the thumb.
Sometimes thickening of the walls of inflamed tendons or swelling in other tunnel areas narrows the passage and puts pressure on the median nerve. The result of this compression may be numbness, weakness, or sometimes pain in the hands and wrists. Some people may feel this pain in the forearm and arm.
This pressure compresses the median nerve, reduces its function, and prevents blood flow to the fingers and hands. If left untreated, compression of the median nerve and lack of blood flow can cause permanent nerve damage.
In carpal tunnel syndrome, pressure is applied to the median nerve of the hand.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common and well-known neuropathy of nerve entrapment because 3 to 6 percent of adults in any statistical population suffer from this syndrome for various reasons, including genetics and frequent hand movements.
Wrist tunnel syndrome was first scientifically defined in the 1800s, and the first surgery to treat it was performed in the 1930s.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome usually begin gradually, with numbness or tingling in the fingers, especially the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger. Some people with this syndrome say that their fingers are swollen and they can not use them. While inflation may be very low or even apparent, inflation may not be visible at all.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome often first appear overnight in one or both hands.
As symptoms worsen, people may feel tingling and numbness in their fingers and hands throughout the day, especially when talking on the phone, reading a book, or driving. Weakness in the hand area can make it difficult to hold small objects or other handicrafts.
In acute or untreated cases of the disease, the muscles of the lower thumb may atrophy and completely disintegrate and disappear. Some people with acute this syndrome cannot distinguish between hot and cold by warming their hands and may burn their fingertips without realizing it.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome:
About 50% of cases of carpal tunnel syndrome are related to hereditary factors. Because the wrist tunnel is narrower in some people, it puts more strain on the median nerve. The average age of people with the disease is between 40 and 50 years, and it rarely occurs in people under 20 years.
Most people do not know what causes carpal tunnel syndrome, and the diagnosis is not definitive even for doctors and researchers. In most cases, the disease is caused by several different factors that increase the pressure on the median nerve and carpal tunnel tendons. Not that the nerve itself is in trouble.
In general, the factors that affect the development of carpal tunnel syndrome are:
- Frequent hand movements such as typing, playing the violin, or any other movement repeatedly when bending the wrist.
- A wrist injury that causes swelling; Such as sprains or fractures
- High blood pressure of the pituitary gland
- Hypothyroidism
- Obesity, diabetes, and pregnancy
The following is a complete list of causes of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Anatomical and Genetic Factors: A fracture or dislocation of the wrist or osteoarthritis that deforms the small bones of the wrist can narrow the space inside the carpal tunnel and put pressure on the median nerve. People whose carpal tunnel is genetically narrower than others are more likely to develop the syndrome. In addition, the syndrome is more common in women because their wrists are usually narrower than their wrists.
Nerve-damaging diseases: Some chronic diseases, such as diabetes, increase the risk of nerve damage, including damage to the median nerve of the carpal tunnel.
Inflammatory diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases may affect the inner layer of the wrist tendons and put pressure on the median nerve.
Medication: Some studies have shown that taking anastrozole, which is used to treat breast cancer, increases the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Pregnancy: During pregnancy and menopause, the volume of body fluids decreases, and as a result, the pressure inside the carpal tunnel increases, and the median nerve is damaged. Carpal tunnel syndrome due to pregnancy usually resolves after this period without the need for surgery and treatment.
Workplace factors: Working with vibrating tools or an assembly line that requires frequent, long bends of the wrist, especially in cold environments, may pressure the median nerve or worsen nerve damage over time. Of course, the scientific evidence in this area is contradictory, and some studies do not consider these factors as a direct cause of carpal tunnel syndrome.
On the other hand, many of us consider typing to be one of the most common causes of this disease, and we probably know people who have stated that the cause of this syndrome is computer work and excessive typing. A study of the effect of wrist position on the carpal tunnel while typing showed that you do not need to worry if you type less than 20 hours a week. But if you type more than 28 hours a week, the risk of developing this syndrome increases. Another study found that people who worked with a computer 12 hours a day were five times more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome.
Other studies have shown that inappropriate computer mice can cause carpal tunnel syndrome. Of course, more research is needed to reach definitive results. Until then, using fewer medical keyboards and protruding mice, resting your hands, and putting less pressure on your fingers as you type can be a good preventative measure.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Wrist tunnel syndrome presents with numbness, weakness, tingling or burning of the fingers or pain in the hands and wrists. The doctor first asks about the symptoms and history of the disease and then performs tests to diagnose the syndrome, which include the following:
Symptoms of tinnitus: In this test, the doctor taps the middle nerve area of the wrist to see if the patient feels a tingling sensation in the fingers.
Experiment: In this test, the doctor asks the patient to stick to the back of his wrist, bend his wrist down, and hold this position for 30 to 60 seconds. This puts pressure on the carpal tunnel and if a person has the syndrome.
Reverse phalanx testing is also used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome. In this test, the patient holds the palms together and holds them up instead of bending the wrists. In this experimental model, in the first 10 seconds after changing the position of the wrist, more pressure is applied to the carpal tunnel, and by maintaining this position, this pressure increases. In contrast, the pressure on the carpal tunnel is milder in the standard Falun test and does not increase after 20 to 30 seconds.
X-ray: If the patient has difficulty performing movement tests or evidence of arthritis or fracture, your doctor may order an X-ray. X-rays are not used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome but only to rule out other causes of pain in the wrist area, including osteoarthritis and fractures.
Nerve and muscle tape (electromyography): This test measures the small electrical discharges created in the muscles. The doctor inserts a thin needle electrode into the involved muscles to assess electrical currents as the muscles contract and relax. This test can detect damage to the muscles under the control of the median nerve and determine if the symptoms of the disease are related to carpal tunnel syndrome.
What happens if carpal tunnel syndrome is not treated?
Early on, the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome appear occasional and mild, which is why some people choose to ignore them. But as time goes on and the disease is ignored, the situation gets worse, and eventually, the work reaches a point where the pain and numbness of the fingers and hands become permanent.
The pain eventually spreads to the arms and shoulders, and over time carpal tunnel syndrome causes atrophy and muscle loss. In these cases, even with treatment and surgery, numbness and muscle weakness in the hand may not go away completely.
Prevention of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Although more than 200 years have passed since the first case of wrist tunnel syndrome was diagnosed, no definitive method has been proposed to prevent this syndrome. But by doing the following, you can minimize the pressure on your hands and wrists and save yourself from one of the most annoying neuropathic diseases.
Reduce pressure on the fingers; If your job requires a keyboard, tap the keys lightly. If you are writing on paper for a long time, use a large pen and do not put too much pressure on your fingers when writing.
Give your hands a short break regularly. Extend your arms gently and bend your fingers back to reduce pressure on the median nerve. If possible, avoid repetitive activities, especially if you work with tools that vibrate or require a lot of force to use them. Even a few minutes of rest per hour can make a big difference.
Be careful of the position of your hands; Be careful not to bend your wrists up or down completely. The best position for the wrist is the middle position, so it is not recommended to use mice with many curvatures and bend the wrist up at a wide-angle. It is best to place your keyboard with your arm or slightly lower and your wrist on the table when using the mouse.
Change your sitting position; Improper sitting position causes the shoulders to bend forward, the neck and shoulder muscles to shorten, and the neck nerves to contract. It can also affect the wrists, fingers, and middle nerves.
Keep your hands warm; If you work in a cold environment, the risk of hand pain and muscle contraction increases. If you can not adjust the ambient temperature, wear fingerless gloves to keep your hands and wrists warm while working.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Carpal tunnel syndrome should be treated as soon as possible after diagnosis. No surgery is needed in cases where the symptoms are mild and the diagnosis is made early. You can splint your hands overnight, avoid irritating activities, rest your hands, physiotherapy, and prescription drugs To reduce stress. The median nerve or alternative therapies such as yoga prevented the syndrome from getting worse.
Unfortunately, in many cases, a person with carpal tunnel syndrome realizes the seriousness of their hand too late, which is why carpal tunnel surgery is one of the most common surgeries in the world. Fortunately, carpal tunnel release surgery has been successful in more than 90% of cases, and many of its symptoms, including tingling and waking up at night, go away quickly. However, finger anesthesia may continue for up to three months after surgery.
Generally, this surgery removes part of the ligament around the wrist to reduce pressure on the median nerve. Surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia or sedation and does not require hospitalization.
The traditional treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome, often performed in Middle Eastern countries, is a liberating surgery in which a 5 cm incision is made in the wrist. Then the transverse ligament is cut to enlarge the tunnel space. The severance of this ligament does not cause any particular problem in the function of the hand’s nerves, and if it is reconstructed, it will become thinner than before. This surgical procedure is usually performed under local and outpatient anesthesia unless the patient has other underlying problems.
Another treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome is endoscopic surgery, reducing the recovery period and postoperative discomfort. But it can also increase the risk of complications and the need for additional surgery.
In this procedure, the surgeon makes one or two incisions of about 1.5 cm in the wrist and palm, then inserts a camera attached to the tube to look at the nerves, ligaments, and tendons, and with a very small knife from It enters. Tube, he tries to cut the ligament.
After surgery and over time, the corners of this ligament usually reconnect. But this time, it creates more space than before. Although symptoms may go away immediately after surgery, full recovery may take months. Some people may develop infections, nerve damage, and pain at the wound site, and in most cases, the hand becomes weak and heals over time. Most people have to change their daily activities for a few weeks after surgery, and some may even need to change jobs.
Recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome is rare after treatment, and less than half of people recover after surgery and normal hand function. In general, early diagnosis and treatment is the best way to prevent permanent nerve damage.